
Review Gatekeeper security technology and runtime protection
macOS offers the Gatekeeper security technology and runtime protection to help ensure that only trusted software runs on a user’s Mac.
When a user downloads and opens an app, a plug-in, or an installer package from outside the App Store, Gatekeeper verifies that the software is from an identified developer, is notarized by Apple to be free of known malicious content, and hasn’t been altered. Gatekeeper also requests user approval before opening downloaded software for the first time to make sure that the user hasn’t been tricked into running executable code they believed to simply be a data file. Gatekeeper also tracks the provenance of files that downloaded software has written. Both the App Store review process and the notarization pipeline are designed to ensure that apps contain no known malware. Therefore by default, all software in macOS is checked for known malicious content the first time it’s opened, regardless of how it arrived on the Mac.
Users and organizations have the option to allow only software installed from the App Store. Alternatively, users can override Gatekeeper policies to open any software unless a device management service restricts it. This includes allowing software signed with alternate identities. Gatekeeper can also be completely disabled, if necessary.
Gatekeeper also protects a Mac even when a benign app triggers the loading of a malicious plug-in without the user’s knowledge. When necessary, Gatekeeper opens apps from randomized, read-only locations. This is designed to prevent the automatic loading of plug-ins distributed alongside the app.
Runtime protection
System files, resources, and the kernel are shielded from a user’s app space. All apps from the App Store are sandboxed to restrict access to data stored by other apps. If an app from the App Store needs to access data from another app, it can do so only by using the APIs and services that macOS provides.
Privacy protections
macOS is designed to keep user’s data safe while respecting the user’s privacy.
Gatekeeper performs online checks to verify if an app contains known malware and whether the developer’s signing certificate is revoked. Apple never combines data from these checks with information about users or their devices, and Apple doesn’t use data from these checks to learn what individual users are using on their devices.
Using an encrypted connection that is resilient to server failures, notarization checks if the app contains known malware.
These security checks have never included the user’s Apple Account or the identity of their device. To further protect privacy, Apple doesn’t log IP addresses associated with Developer ID certificate checks, and makes sure that any collected IP addresses are removed from logs.
If a user wants to open an app that hasn’t been notarized or is from an unidentified developer
Running software that hasn’t been signed and notarized might expose the user’s Mac and personal information to malware that can harm the Mac or compromise their—and their organization’s—privacy.
If they’re certain that an app that they want to open is from a trustworthy source and hasn’t been tampered with, they might be able to temporarily override the Mac security settings to open it.
On the Mac, choose Apple menu > System Settings, then click Privacy & Security in the sidebar.
Scroll down, and click the Open Anyway button to confirm your intent to open or install the app.
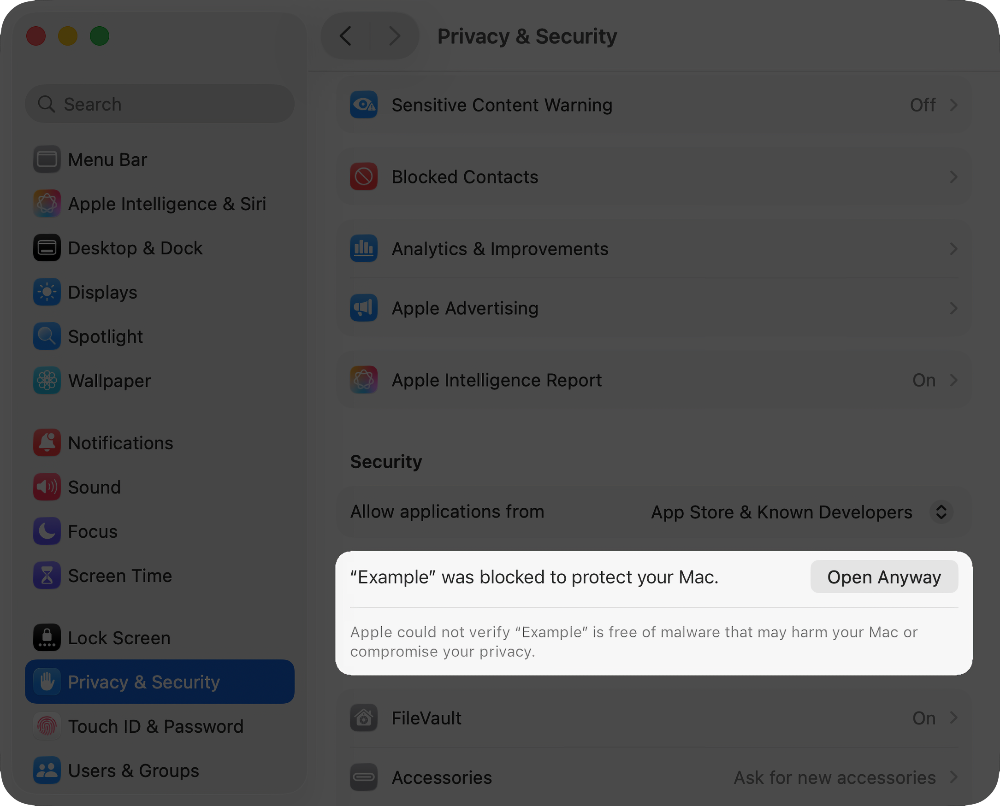
The warning prompt reappears and, if you’re absolutely sure that you want to open the app anyway, you can click Open.
The app is now saved as an exception to your security settings, and you can open it in the future by double-clicking it, just as you can any authorized app.
Change the app security settings on a Mac
Note: These settings might not be available if the Mac is managed by a device management service.
On the Mac, choose Apple menu > System Settings, then click Privacy & Security in the sidebar.
Scroll down to Security.
Under “Allow apps downloaded from,” select an option:
App Store: Allow only apps that have been downloaded from the App Store.
App Store and identified developers: Allow apps that have been downloaded from the App Store and from developers identified by Apple.