Intro to device storage and content sharing
You might need to assist with troubleshooting storage access issues and guiding users through storage optimization. By checking storage usage, you can help users identify what’s taking up space, whether it’s large files, system data, or unused apps, and guide them in freeing up space or upgrading storage if needed.
Managing device content and device storage on a Mac is a key part of maintaining system performance and helping users stay productive.
See used and available storage space on a Mac to quickly diagnose performance issues, installation problems, or system warnings related to low storage space. When their Mac runs out of storage, a user can experience slow performance, failed updates, or app crashes.
In addition to local storage, iCloud storage allows users to efficiently manage storage space by automatically backing up and syncing files across all Apple devices. By storing photos, documents, and app data in iCloud, users free up local storage on their devices while ensuring easy access to their content anytime, anywhere. Additionally, iCloud’s optimization features help manage device storage by keeping only recent or frequently used items locally, while older files are stored in the cloud.
Whether it’s freeing up space, identifying large files, or using built-in tools like Disk Utility and Storage Management, having a solid understanding of these tasks ensures that you can resolve issues quickly.
Mounting, unmounting, and ejecting storage
You should be familiar with how to mount, unmount, and eject storage devices on a Mac. Mounting makes a device accessible to the system, while unmounting and ejecting ensure that data is properly saved and the device can be safely removed. You may encounter situations where a device fails to appear, won’t eject, or shows errors. This knowledge is especially important when supporting tasks like software installations, data transfers, or backup operations. If you can’t eject a device on a Mac, try these solutions using Disk Utility on Mac.
Sharing
Sharing on a Mac enables collaboration and resource access across devices and networks by offering features such as file, screen, printer, and internet sharing. A correct setup ensures secure and efficient access to files, screen sharing, and services, while misconfigurations can cause connectivity problems or pose security risks. Managing sharing permissions, network configurations, and user access is key to maintaining system integrity. Users connect to shared computers and file servers on the network, including both Mac and Windows systems with file sharing enabled, as well as servers using protocols like SMB. Connections can be made by browsing available devices or entering the server’s network address directly.
For more information, see Share your Mac screen, files, and services with other users on your network in the Mac User Guide.
File sharing using AirDrop
AirDrop allows users to quickly transfer files between Apple devices, but it can also lead to unexpected storage space usage if large files are received and saved. On a Mac, some items are automatically saved in the Downloads folder. You may also have the option to choose where to save items. You should know how to locate and manage these files, advise users on organizing or offloading large transfers, and ensure that shared content doesn’t go unnoticed or accumulate over time. For more information about AirDrop, see to Use AirDrop to send items to nearby Apple devices.
If AirDrop can’t discover other devices
What to look for:
Devices don’t appear in the AirDrop window.
Steps to take:
Make sure that both the sender and recipient have Wi-Fi and Bluetooth turned on and that both are using an iPhone, iPad, or Mac.
Set AirDrop to Everyone or Contacts Only in the Finder or Apple menu > System Settings > General > AirDrop & Handoff.
Check that devices are within 30 feet (10 meters) of one another.
Check that the receiving device is awake and unlocked.
Restart both devices to reset networking services.
If file transfer doesn’t complete or hangs
What to look for:
Waiting or failed transfer messages
Steps to take:
Send smaller files first to test whether larger files are the issue.
Verify that both devices are signed in with an Apple Account for iCloud (for Contacts Only sharing) and that an Apple Account email address or phone numbers exist in their Contacts.
Try switching the AirDrop setting to Everyone for more reliability during troubleshooting.
If AirDrop is missing from the Share sheet
What to look for:
AirDrop doesn’t appear as a sharing option.
Steps to take:
Go to Finder > Go > AirDrop, and set AirDrop to Everyone or Contacts Only.
Check Apple menu > System Settings > General > AirDrop & Handoff, and ensure that AirDrop is turned on.
Check Screen Time settings or device management profiles that might be restricting AirDrop use.
If the device shows as unavailable
What to look for:
The target device shows up but is dimmed.
Steps to take:
Ensure that the other device isn’t busy with another AirDrop transfer.
Restart the target device.
Temporarily set AirDrop to Everyone and try again.
If there are firewall or privacy restrictions
What to look for:
System settings block AirDrop.
Steps to take:
Verify that Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are turned on.
Check whether AirDrop is managed by a device management service.
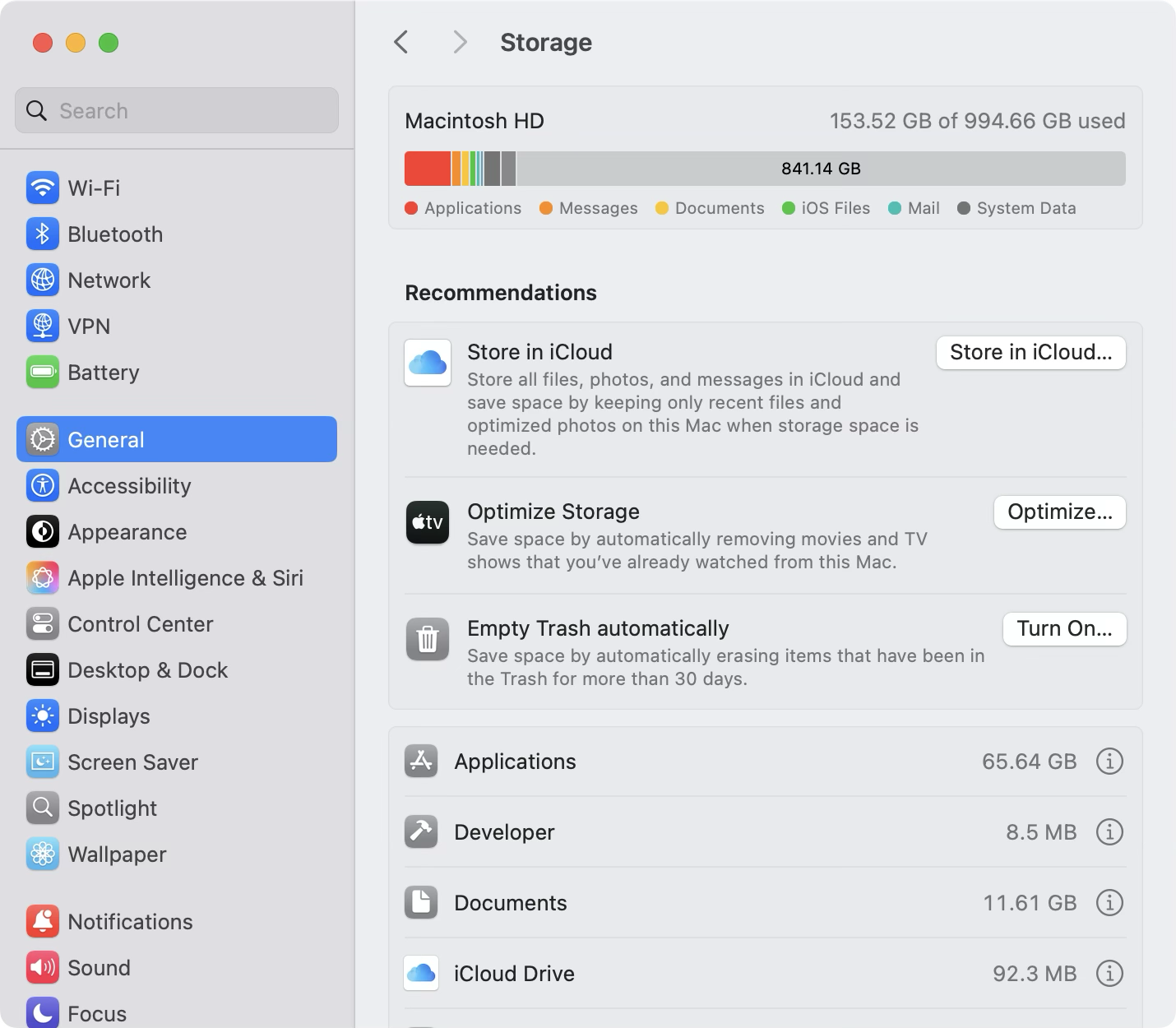
Managing storage using System Settings
To find storage information about a Mac, choose Apple menu > System Settings > General > Storage. The Storage tab breaks down space usage by category, like apps, documents, and system files, making it easier to pinpoint what’s consuming the most space. Use this information to help users delete unnecessary files, move content to external drives, or manage large apps. By actively monitoring storage this way, you can prevent slow performance, failed updates, and storage-related support calls that disrupt user productivity.