Modifying this control will update this page automatically
Final Cut Pro User Guide for Mac
- Welcome
- What’s new
-
- Intro to importing media
- If it’s your first import
- Organize files during import
-
- Import from Image Playground
- Import from iMovie for macOS
- Import from iMovie for iOS or iPadOS
- Import from Final Cut Pro for iPad
- Import from Final Cut Camera
- Import from Photos
- Import from Music
- Import from Apple TV
- Import from Motion
- Import from GarageBand and Logic Pro
- Import using workflow extensions
- Record into Final Cut Pro
- Memory cards and cables
- Supported media formats
-
- Intro to effects
-
- Intro to transitions
- How transitions are created
- Add transitions and fades
- Quickly add a transition with a keyboard shortcut
- Set the default duration for transitions
- Delete transitions
- Adjust transitions in the timeline
- Adjust transitions in the inspector and viewer
- Merge jump cuts with the Flow transition
- Adjust transitions with multiple images
- Modify transitions in Motion
- Add adjustment clips
-
- Add storylines
- Use the precision editor
- Conform frame sizes and rates
- Use XML to transfer projects
- Glossary
- Copyright and trademarks
audio waveforms
Audio waveforms are visual representations of the actual sound. Audio waveforms appear in clips in the following ways:
As the bottom portion of a video clip
As a detached or audio-only clip
An audio waveform’s amplitude and length change according to the underlying sound’s volume and duration. A short, loud sound such as a drum beat has a sharp, peaked waveform, whereas low-level crowd noise has a lower, more uniform waveform. These properties make it easier to find specific edit points when trimming clips or keyframing effects.
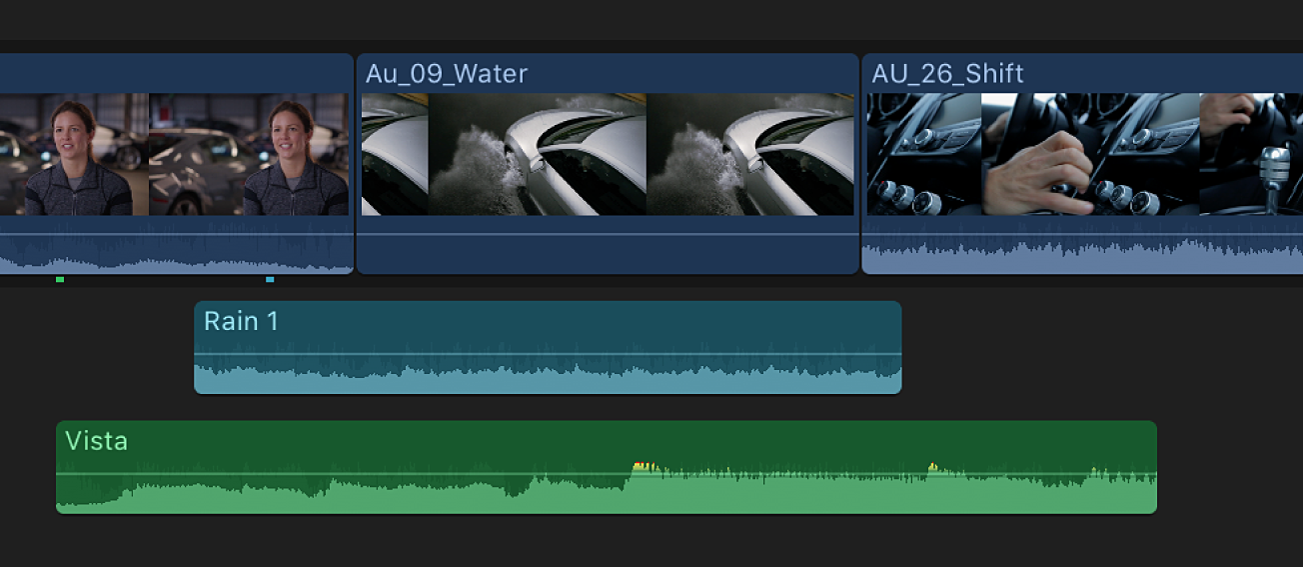
You edit audio clips in the timeline by first listening to a clip’s audio through playback and skimming, and then applying changes to the clip, using the waveform as a reference.
Thanks for your feedback.