Apple Platform Deployment
- Welcome
- Intro to Apple Platform Deployment
- What’s new
-
-
- Declarative status reports
- Declarative app configuration
- Authentication credentials and identity asset declaration
- Background task management declarative
- Calendar declarative configuration
- Certificates declarative configuration
- Contacts declarative configuration
- Exchange declarative configuration
- Google Accounts declarative configuration
- LDAP declarative configuration
- Legacy interactive profile declarative configuration
- Legacy profile declarative configuration
- Mail declarative configuration
- Math and Calculator app declarative configuration
- Passcode declarative configuration
- Passkey Attestation declarative configuration
- Safari browsing management declarative configuration
- Safari extensions management declarative configuration
- Screen Sharing declarative configuration
- Service configuration files declarative configuration
- Software Update declarative configuration
- Software Update settings declarative configuration
- Storage management declarative configuration
- Subscribed Calendars declarative configuration
-
-
- Accessibility payload settings
- Active Directory Certificate payload settings
- AirPlay payload settings
- AirPlay Security payload settings
- AirPrint payload settings
- App Lock payload settings
- Associated Domains payload settings
- Automated Certificate Management Environment (ACME) payload settings
- Autonomous Single App Mode payload settings
- Calendar payload settings
- Cellular payload settings
- Cellular Private Network payload settings
- Certificate Preference payload settings
- Certificate Revocation payload settings
- Certificate Transparency payload settings
- Certificates payload settings
- Conference Room Display payload settings
- Contacts payload settings
- Content Caching payload settings
- Directory Service payload settings
- DNS Proxy payload settings
- DNS Settings payload settings
- Dock payload settings
- Domains payload settings
- Energy Saver payload settings
- Exchange ActiveSync (EAS) payload settings
- Exchange Web Services (EWS) payload settings
- Extensible Single Sign-on payload settings
- Extensible Single Sign-on Kerberos payload settings
- Extensions payload settings
- FileVault payload settings
- Finder payload settings
- Firewall payload settings
- Fonts payload settings
- Global HTTP Proxy payload settings
- Google Accounts payload settings
- Home Screen Layout payload settings
- Identification payload settings
- Identity Preference payload settings
- Kernel Extension Policy payload settings
- LDAP payload settings
- Lights Out Management payload settings
- Lock Screen Message payload settings
- Login Window payload settings
- Managed Login Items payload settings
- Mail payload settings
- Network Usage Rules payload settings
- Notifications payload settings
- Parental Controls payload settings
- Passcode payload settings
- Printing payload settings
- Privacy Preferences Policy Control payload settings
- Relay payload settings
- SCEP payload settings
- Security payload settings
- Setup Assistant payload settings
- Single Sign-on payload settings
- Smart Card payload settings
- Subscribed Calendars payload settings
- System Extensions payload settings
- System Migration payload settings
- Time Machine payload settings
- TV Remote payload settings
- Web Clips payload settings
- Web Content Filter payload settings
- Xsan payload settings
-
- Glossary
- Document revision history
- Copyright and trademarks

Lock and locate Apple devices
With a device management service, you can lock an Apple device remotely, and even locate a lost or stolen iPhone or iPad that is in Lost Mode.
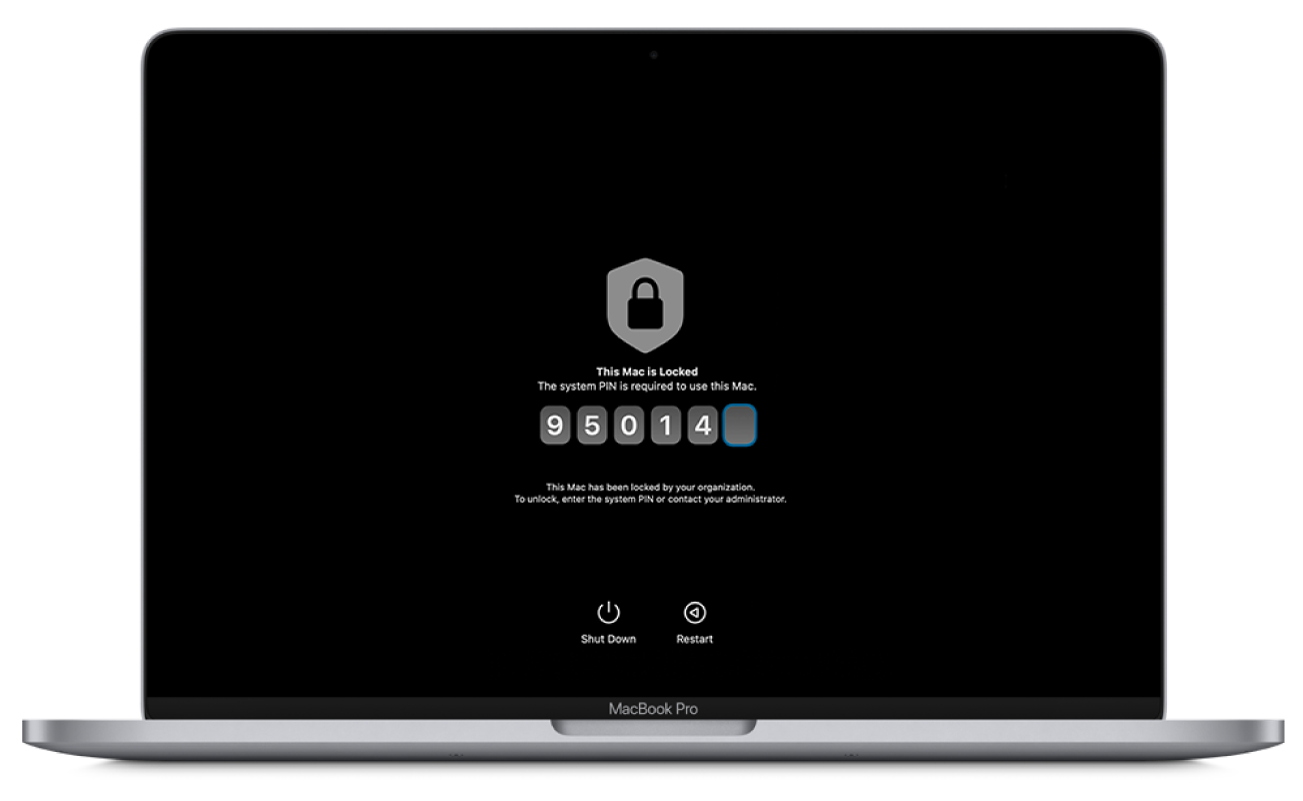
Lock devices
There are three ways you can remotely lock an Apple device: with Activation Lock, by locking a Mac remotely, or by using Managed Lost Mode.
Activation Lock: When a user turns on Activation Lock, it’s difficult for someone else to use or sell an iPhone, iPad, Mac, or Apple Watch if it’s ever lost or stolen. If you use a device management service that supports Activation Lock, you can manage it for devices your organization owns.
Lock a Mac: Device management service administrators can lock a Mac with a six-digit personal identification number (PIN) and include a short message. After sending the command to the device, it restarts and the user can see the message. The user can’t restart into macOS until they enter the PIN and the Mac validates it.
Note: Locking a Mac computer with Apple silicon requires macOS 11.5 or later.
Managed Lost Mode: Managed Lost Mode for supervised iPhone or iPad locks the current user out of the device until Managed Lost Mode is turned off.
Locate lost or stolen supervised devices
Device management services can remotely place a supervised iPhone or iPad in Lost Mode (called Managed Lost Mode). Turning on Managed Lost Mode locks the current user out of the device. The Lock Screen displays a message that the device management service administrator can customize, such as displaying a phone number to call if the device is found. Also, when a device is in Managed Lost Mode, a device management service can remotely query for the device’s location (even if location services are off) and, optionally, play a sound. Managed Lost Mode automatically enables Low Power Mode to help extend the device’s battery life, and doesn’t require Find My to be turned on.
When an administrator turns off Managed Lost Mode, which is the only way the device can exit the mode, the user receives a notification that the device management service administrator has turned off Managed Lost Mode and collected the device’s location through either a message on the Lock Screen or an alert on the Home Screen.