Logic Pro User Guide for iPad
- Welcome
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Working areas
- Work with the menu bar
- Work with function buttons
- Work with numeric values
- Undo and redo edits in Logic Pro for iPad
-
- Intro to tracks
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Choose the default region type for a software instrument track
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Reorder tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Use the tuner on an audio track
- Show the output track in the Tracks area
- Delete tracks
- Edit track parameters
- How to get help
-
- Intro to recording
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Merge software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Route MIDI internally to software instrument tracks
- Record with Low Latency Monitoring mode
- Use the metronome
- Use the count-in
-
- Intro to arranging
-
- Intro to regions
- Select regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Remove gaps between regions
- Delay region playback
- Trim regions
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Mute regions
- Split and join regions
- Stretch regions
- Separate a MIDI region by note pitch
- Bounce regions in place
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Normalize audio regions in the Tracks area in Logic Pro for iPad
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Convert a MIDI region to a Session Player region or a pattern region
- Replace a MIDI region with a Session Player region in Logic Pro for iPad
- Rename regions
- Change the color of regions
- Delete regions
-
- Intro to chords
- Add and delete chords
- Select chords
- Cut, copy, and paste chords
- Move and resize chords
- Loop chords on the Chord track
- Color chords on the Chord track
- Edit chords
- Work with chord groups
- Use chord progressions
- Change the chord rhythm
- Choose which chords a Session Player region follows
- Analyze the key signature of a range of chords
- Use Chord ID to analyze the chords in an audio or MIDI region
- Create fades on audio regions
- Extract vocal and instrumental stems with Stem Splitter
- Access mixing functions using the Fader
-
- Intro to Step Sequencer
- Use Step Sequencer with Drum Machine Designer
- Chords and pitch in Step Sequencer
- Record Step Sequencer patterns live
- Step record Step Sequencer patterns
- Load and save patterns
- Modify pattern playback
- Edit steps
- Edit rows
- Edit Step Sequencer pattern, row, and step settings in the inspector
- Customize Step Sequencer
-
- Intro to mixing
-
- Channel strip types
- Channel strip controls
- Peak level display and clipping
- Set channel strip volume
- Set channel strip input format
- Set the output for a channel strip
- Set channel strip pan position
- Mute and solo channel strips
- Reorder channel strips
- Replace a patch on a channel strip using drag and drop
- Work with plug-ins in the Mixer
- Search for plug-ins in the Mixer
-
-
- Effect plug-ins overview
-
- Instrument plug-ins overview
-
- ES2 overview
-
- Modulation overview
- Use the Mod Pad
-
- Vector Envelope overview
- Use Vector Envelope points
- Use Vector Envelope solo and sustain points
- Set Vector Envelope segment times
- Vector Envelope XY pad controls
- Vector Envelope Actions menu
- Vector Envelope loop controls
- Vector Envelope point transition shapes
- Vector Envelope release phase behavior
- Use Vector Envelope time scaling
- Modulation source reference
- Via modulation source reference
- Use macro controls
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Save a preset
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Low, bandpass, and highpass filters
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
- Sampler
- Studio Piano
- Copyright and trademarks
YardStick controls in Logic Pro for iPad
The YardStick model builds on the QRS model with updated algorithms that enhance the accuracy of acoustic simulations and provide more precise control over reverb characteristics. It includes improved controls for early reflections, diffusion, and modulation. This design supports more dynamic and evolving reverb effects, allowing for the creation of complex reverb tails with greater depth and richness.
The main view of the YardStick contains the most commonly used parameters.
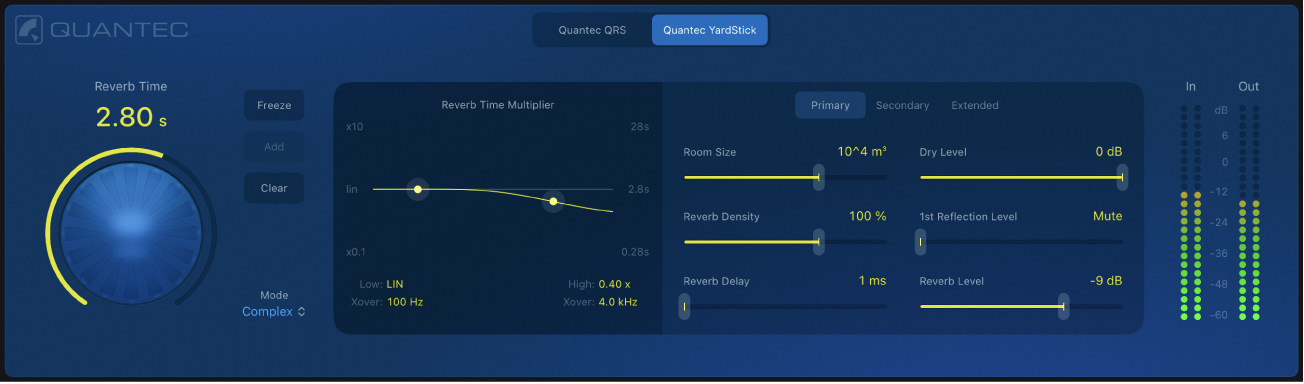
YardStick main parameters
Quantec logo: Tap the logo to open the Quantec Room Simulator information dialog, which provides details about the inventor and the development of the QRS and YardStick reverbs.
 Reverb model buttons: Select a reverb model: QRS or YardStick. The QRS is the original classic vintage unit, and the YardStick represents the evolution and modernization of Quantec’s reverb technology.
Reverb model buttons: Select a reverb model: QRS or YardStick. The QRS is the original classic vintage unit, and the YardStick represents the evolution and modernization of Quantec’s reverb technology. Reverb Time knob and field: Adjust the reverb duration in conjunction with the Room Size control. The ring around the knob displays the reverb time range based on the chosen room size.
Reverb Time knob and field: Adjust the reverb duration in conjunction with the Room Size control. The ring around the knob displays the reverb time range based on the chosen room size. Freeze button: Use Freeze to capture and sustain the reverb tail, an ideal way to create organic soundscapes. Once captured, the audio routes only through Freeze, bypassing the main reverb.
Freeze button: Use Freeze to capture and sustain the reverb tail, an ideal way to create organic soundscapes. Once captured, the audio routes only through Freeze, bypassing the main reverb.Add button: Touch and hold to capture another portion of the reverb tail. How long you hold determines how much audio is captured and added to the existing freeze effect. Repeat to layer sounds.
Clear button: Tap to clear the audio captured in the Freeze effect.
Mode pop-up menu: Choose from three levels of reverb complexity: Complex offers rich, detailed reflections for immersive sound; Medium provides balanced, natural reverberation; Simple delivers a subtle effect.
In meter: Displays the level of the incoming audio signal sent to the reverb effect. This helps monitor signal strength and prevent distortion in the source signal feeding the reverb.
Out meter: Displays the combined output level of all signals within the plug-in.
YardStick reverb time multiplier parameters
Use the multiplier curve to adjust and visualize the room’s reverb response across the frequency spectrum. Additionally, the YardStick provides precise control over the crossover points between low and high frequencies, giving you more flexibility in shaping the overall sound. This feature lets you create either brighter or darker reverbs, simulating rooms with more reflective or absorbent walls.
The graph shows frequency on the x-axis and reverb time on the y-axis. The right scale reflects the reverb time, which you change by tuning the Reverb Time knob. Two control points adjust reverb time for low frequencies (below 1 kHz) and high frequencies (above 1 kHz) relative to the set reverb time. The left scale indicates this factor, ranging from a maximum increase of 10 x to a decrease of 0.1 x.
These multipliers offer precise control over the reverb tail’s frequency response, achieving a natural room reverb effect that can’t be replicated with EQ alone.
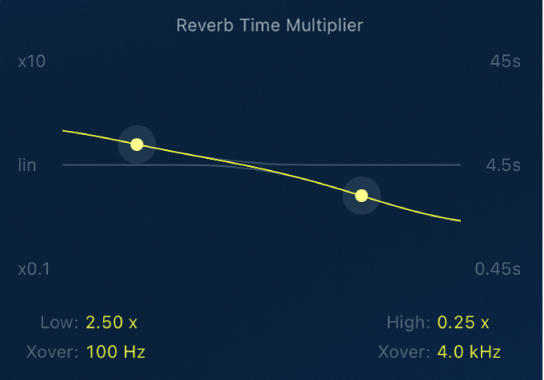
Low and Xover control point and fields: Drag the control point vertically to adjust the reverb time multiplier for low frequencies and horizontally to set the crossover (Xover) frequency.
High and Xover control point and fields: Drag the control point vertically to adjust the reverb time multiplier for high frequencies and horizontally to set the crossover frequency.
YardStick primary parameters
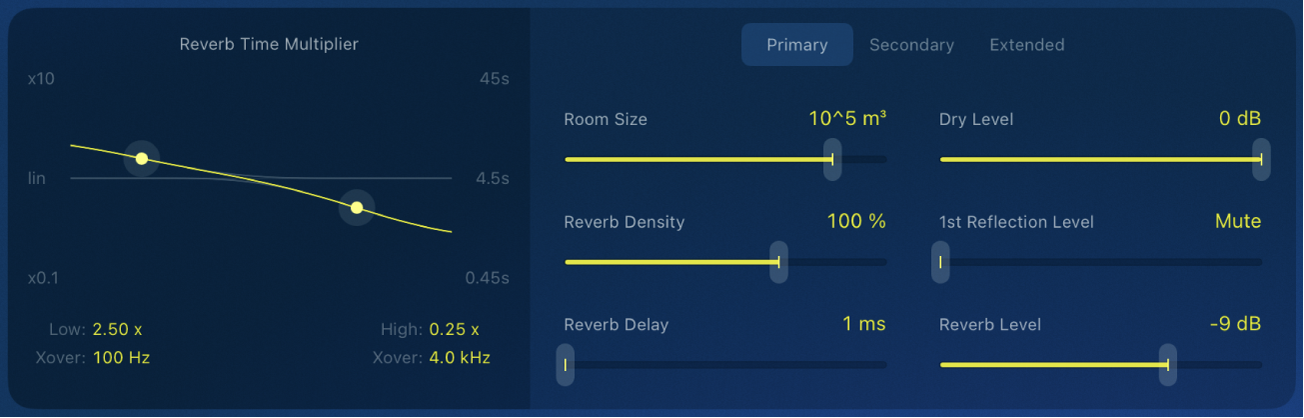
Primary button: Access frequently used reverb settings.
Room Size slider and field: Set the room dimensions in cubic meters, from 1 m³ to 1,000,000 m³. Changing this parameter also adjusts the range of the Reverb Time knob.
Reverb Density slider and field: Adjust the reflected energy of the room’s natural resonances. Density values above 100% balance a high initial reflection density with a slight risk of a metallic-sounding reverb tail.
Reverb Delay slider and field: Increasing the Reverb Delay value introduces a delay between the source signal and the reverb onset. Use this parameter to add up to 200 ms of delay, affecting spatial perception and timing in the mix.
Dry Level slider and field: Set the level of the dry signal at the plug-in output independently from the first reflection and the reverb tail.
1st Reflection Level slider and field: Set the level of the first reflection at the plug-in output independently from the dry signal and the reverb tail. Raising the level adds intimacy and presence, and lowering it creates a more open, spacious feel, shaping the reverb’s depth.
 Reverb Level slider and field: Set the level of the reverb tail at the plug-in output independently from the dry signal and the first reflection.
Reverb Level slider and field: Set the level of the reverb tail at the plug-in output independently from the dry signal and the first reflection.
YardStick secondary parameters
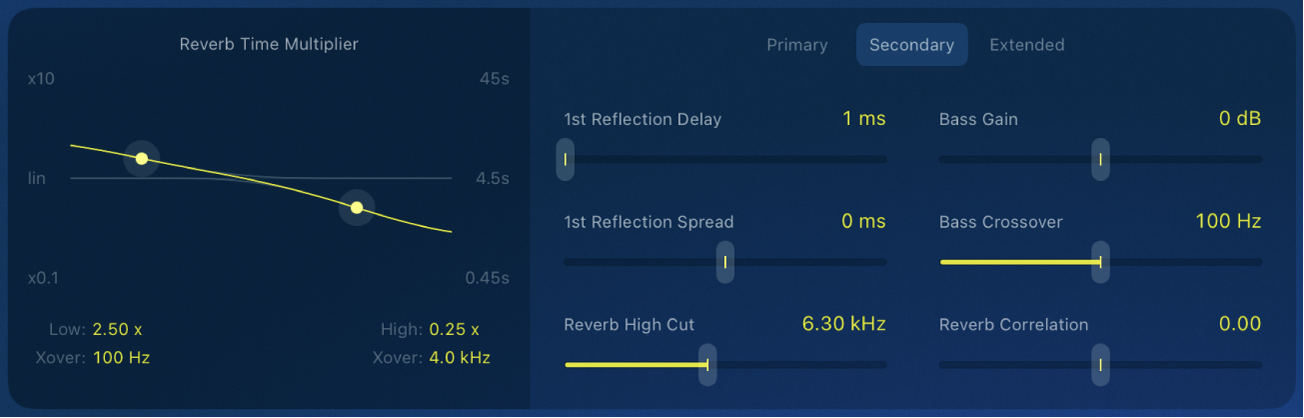
Secondary button: Access additional settings that offer more detailed adjustments and fine-tuning options. Note that some options are unavailable when using the Quantec Room Simulator on a mono channel strip.
1st Reflection Delay slider and field: Adjust the time between the direct sound and the first reflection to influence the spatial perception of the room.
1st Reflection Spread slider and field: Adjust the time difference of the first reflection between the left and right stereo channels to affect the stereo width of the reflection.
Reverb High Cut slider and field: Adjust the cutoff frequency of the high-cut filter applied to the output of the reverb tail. This control limits the high-frequency content, reducing brightness and creating a more subdued or warmer effect.
Bass Gain slider and field: Adjust the low-frequency content in the reverb signal. Use this control to increase or decrease bass frequencies. Combined with the Bass Crossover parameter, it shapes the level of bass frequencies.
Bass Crossover slider and field: Set the cutoff frequency to control which low frequencies are affected by the bass gain. This lets you precisely shape the bass content in the reverb.
Reverb Correlation slider and field: Adjust the stereo width of the reverb effect. Changing this parameter alters how the reverb is spread across the stereo field, ranging from a narrow, focused effect to a wide, immersive sound.
YardStick extended parameters

Extended button: Access advanced settings for precise fine-tuning and in-depth customization. Note that some options are unavailable when using the Quantec Room Simulator on a mono channel strip.
Dry Source pop-up menu: Set the channel assignment for the output of the dry signal. Maintain the original order (L R) or swap the left and right channels (R L). This setting doesn’t affect how the stereo signal is routed to the reverb effect input and is unavailable when operating the plug-in in mono.
1st Reflection Source pop-up menu: Set the channel assignment for the output of the first reflection. Maintain the original order (L R) or swap the left and right channels (R L).
L Correlation Pattern pop-up menu: Choose predefined virtual microphone positions in the reverb chamber for the left channel. Using the same number for both channels results in a mono output. The number of correlation patterns depends on the chosen mode (Simple, Medium, or Complex). Choose Off to mute the Reverb output channel, independently of the dry and first reflection output.
R Correlation Pattern pop-up menu: Choose predefined virtual microphone positions in the reverb chamber for the right channel. Using the same number for both channels results in a mono output. The number of correlation patterns depends on the chosen mode (Simple, Medium, or Complex). Choose Off to mute the Reverb output channel, independently of the dry and first reflection output.
Subsonic button: Turn off Subsonic to filter out inaudible low frequencies in the reverb input that can cause rumble and unwanted low-end buildup. Turn on Subsonic to process the unfiltered input signal.
Download this guide: PDF