Logic Pro User Guide for iPad
- Welcome
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Working areas
- Work with the menu bar
- Work with function buttons
- Work with numeric values
- Undo and redo edits in Logic Pro for iPad
-
- Intro to tracks
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Choose the default region type for a software instrument track
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Reorder tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Use the tuner on an audio track
- Show the output track in the Tracks area
- Delete tracks
- Edit track parameters
- How to get help
-
- Intro to recording
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Merge software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Route MIDI internally to software instrument tracks
- Record with Low Latency Monitoring mode
- Use the metronome
- Use the count-in
-
- Intro to arranging
-
- Intro to regions
- Select regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Remove gaps between regions
- Delay region playback
- Trim regions
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Mute regions
- Split and join regions
- Stretch regions
- Separate a MIDI region by note pitch
- Bounce regions in place
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Normalize audio regions in the Tracks area in Logic Pro for iPad
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Convert a MIDI region to a Session Player region or a pattern region
- Replace a MIDI region with a Session Player region in Logic Pro for iPad
- Rename regions
- Change the color of regions
- Delete regions
-
- Intro to chords
- Add and delete chords
- Select chords
- Cut, copy, and paste chords
- Move and resize chords
- Loop chords on the Chord track
- Color chords on the Chord track
- Edit chords
- Work with chord groups
- Use chord progressions
- Change the chord rhythm
- Choose which chords a Session Player region follows
- Analyze the key signature of a range of chords
- Use Chord ID to analyze the chords in an audio or MIDI region
- Create fades on audio regions
- Extract vocal and instrumental stems with Stem Splitter
- Access mixing functions using the Fader
-
- Intro to Step Sequencer
- Use Step Sequencer with Drum Machine Designer
- Chords and pitch in Step Sequencer
- Record Step Sequencer patterns live
- Step record Step Sequencer patterns
- Load and save patterns
- Modify pattern playback
- Edit steps
- Edit rows
- Edit Step Sequencer pattern, row, and step settings in the inspector
- Customize Step Sequencer
-
- Intro to mixing
-
- Channel strip types
- Channel strip controls
- Peak level display and clipping
- Set channel strip volume
- Set channel strip input format
- Set the output for a channel strip
- Set channel strip pan position
- Mute and solo channel strips
- Reorder channel strips
- Replace a patch on a channel strip using drag and drop
- Work with plug-ins in the Mixer
- Search for plug-ins in the Mixer
-
-
- Effect plug-ins overview
-
- Instrument plug-ins overview
-
- ES2 overview
-
- Modulation overview
- Use the Mod Pad
-
- Vector Envelope overview
- Use Vector Envelope points
- Use Vector Envelope solo and sustain points
- Set Vector Envelope segment times
- Vector Envelope XY pad controls
- Vector Envelope Actions menu
- Vector Envelope loop controls
- Vector Envelope point transition shapes
- Vector Envelope release phase behavior
- Use Vector Envelope time scaling
- Modulation source reference
- Via modulation source reference
- Use macro controls
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Save a preset
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Low, bandpass, and highpass filters
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
- Sampler
- Studio Piano
- Copyright and trademarks
Pitch Shifter in Logic Pro for iPad
Pitch Shifter provides a simple way to combine a pitch-shifted version of the signal with the original signal. See Use Pitch Shifter.
To add Pitch Shifter to your project, choose Pitch > Pitch Shifter in a channel strip Audio Effect plug-in menu or the Plug-ins area. See Intro to plug-ins. Also see Add, replace, reorder, and remove plug-ins in the Plug-ins area and Work with plug-ins in the Mixer.
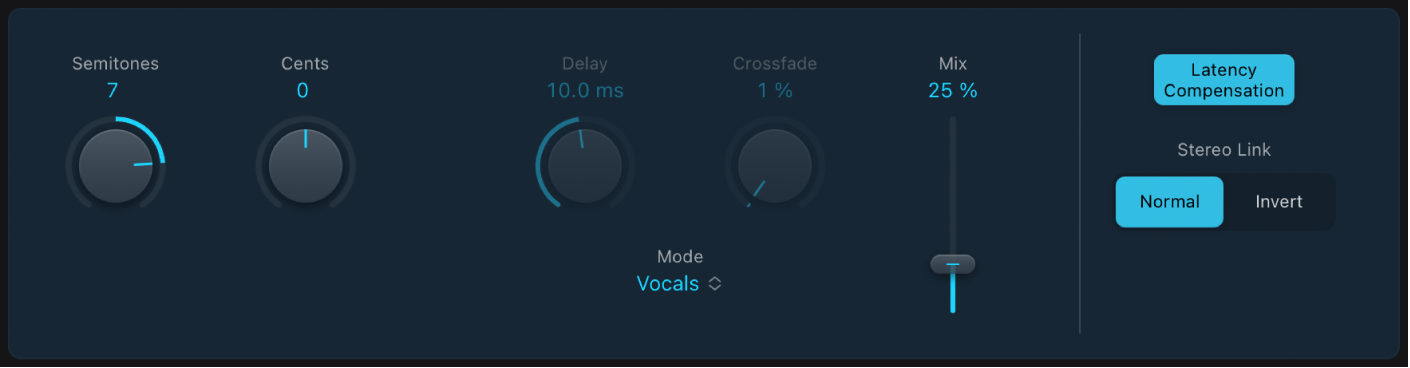
Pitch Shifter parameters
 Semitones knob and field: Set the pitch shift value in semitones.
Semitones knob and field: Set the pitch shift value in semitones. Cents knob and field: Control detuning of the pitch shift value in cents (1/100th of a semitone).
Cents knob and field: Control detuning of the pitch shift value in cents (1/100th of a semitone).Mode pop-up menu: Choose an algorithm to determine how timing is derived.
Drums: Maintains the groove (rhythmic feel) of the source signal.
Speech: Provides a balance between both the rhythmic and harmonic aspects of the signal. This is suitable for complex signals such as spoken-word recordings, rap, and hybrid signals such as rhythm guitar.
Vocals: Retains the intonation of the source, making it well-suited for signals that are inherently harmonic or melodious, such as string pads.
Manual: Uses the settings of the Delay, Crossfade, and Stereo Link parameters.
Pitch Tracking: Follows the pitch of incoming audio material.
Note: The Delay and Crossfade parameters are active only when Manual is chosen from the Mode pop-up menu.
Delay knob and field: Set the amount of delay applied to the input signal. The lower the frequencies of the input signal, the higher (longer) a delay time is required—to effectively pitch shift the signal.
Crossfade knob and field: Set the range (shown as a percentage of the original signal) used to analyze the input signal.
 Mix control and field: Set the balance between the effect and original signals.
Mix control and field: Set the balance between the effect and original signals.Latency Compensation button: Turn on to compensate for delays that may be introduced by some algorithms with particular types of source material.
Stereo Link buttons: Normal retains the source stereo signals. Invert swaps (inverts) stereo channel signals, with right channel processing occurring on the left, and vice versa.
Download this guide: PDF