
Add and edit effect plug-ins in GarageBand on Mac
Effects let you shape and enhance the sound of your music in a variety of ways. Many familiar sounds in popular music are created using effects.
Each patch has up to four built-in effect plug-ins. You can add effect plug-ins to a patch, turn them on or off, reorder them, and remove them in the Plug-ins area. You can also adjust effect settings by opening the plug-in window for the effect.
Effect types
GarageBand includes a variety of studio-quality effect plug-ins that you can use in your projects:
Compressor: A compressor adjusts the volume of the audio signal to smooth out sudden level changes. Compressors can add punch and definition to a track or an entire song, and can make it sound better when played on audio equipment with a narrow dynamic range.
Delay: A delay effect repeats a sound like an echo. It can add a subtle sense of space to a sound, or can create the impression that a voice or an instrument is in a large room or cavern. You can also use delay effects to double individual sounds to resemble a group of instruments playing the same melody, to generate rhythmic effects, or to enhance the stereo position of tracks in your songs.
Distortion: Distortion effects, which include amp simulation and overdrive, change the tone of the original sound to re-create analog or digital distortion. Vacuum tubes were used in audio amplifiers before the development of digital audio technology and are still used in some amplifiers today. Overdriven tube amps produce a musically pleasing distortion that has become a familiar part of the sound of rock and pop music. Digital distortion effects provide another type of distortion that can be used to modify voice and other tracks to produce an intense, unnatural tone, or to create sound effects.
EQ: EQ (short for equalization) is a powerful and versatile effect that lets you change the level of selected frequencies in a sound. You can use EQ to make both subtle and dramatic changes to the sound of an audio file, an instrument, a vocal performance, or an entire project. EQ is one of the most commonly used effects in popular music.
All EQs are specialized audio filters that allow certain frequencies to pass through unchanged while raising (boosting) or lowering (cutting) the level of other frequencies. GarageBand patches have an EQ effect that combines several filters in one unit, so you can view and edit multiple frequency bands within an overall frequency spectrum.
Modulation: Modulation effects include chorus, flangers, and phasers. Like delay effects, they repeat the sound, but with a very short delay time in milliseconds, and in addition, they shift or modulate when the repeated signal plays back. The signal can also be detuned relative to the original. Modulation effects are used to add motion and depth to your sound.
Noise Gate: A noise gate reduces low-level noise by cutting off the sound when it falls below a certain minimum level (known as the threshold). It is often used as the first in a series of effects to help reduce input noise. You can select the Noise Gate checkbox on an audio track to load that plug-in.
Reverb: Reverb simulates the natural reflections of a sound in a surrounding space. It can add definition and presence to voices and instruments, can add ambience to a sound, or can simulate different rooms and other acoustic environments.
Many GarageBand patches include screen controls for reverb effects in the Smart Controls, typically named Ambience and Reverb. When the screen controls are active (not set to zero), these reverb effects modify the sound of the track. The sound of these effects can be edited using the Master Effects screen controls, after choosing one of the effects from the upper pop-up menu in the Master Effects section. In the pop-up menu, the name reflects the name of the screen control used in the patch.
Others: GarageBand includes other types of effects, such as amp models, filters, pitch shifters, and other specialized effects.
Add an effect plug-in
In GarageBand on Mac, in the Plug-ins area, click an empty plug-in slot, choose an effect category, then choose a plug-in from the submenu.
When all plug-in slots are occupied, you can click in the space between plug-ins, above the first plug-in, or below the last plug-in, choose a category, then choose a plug-in.
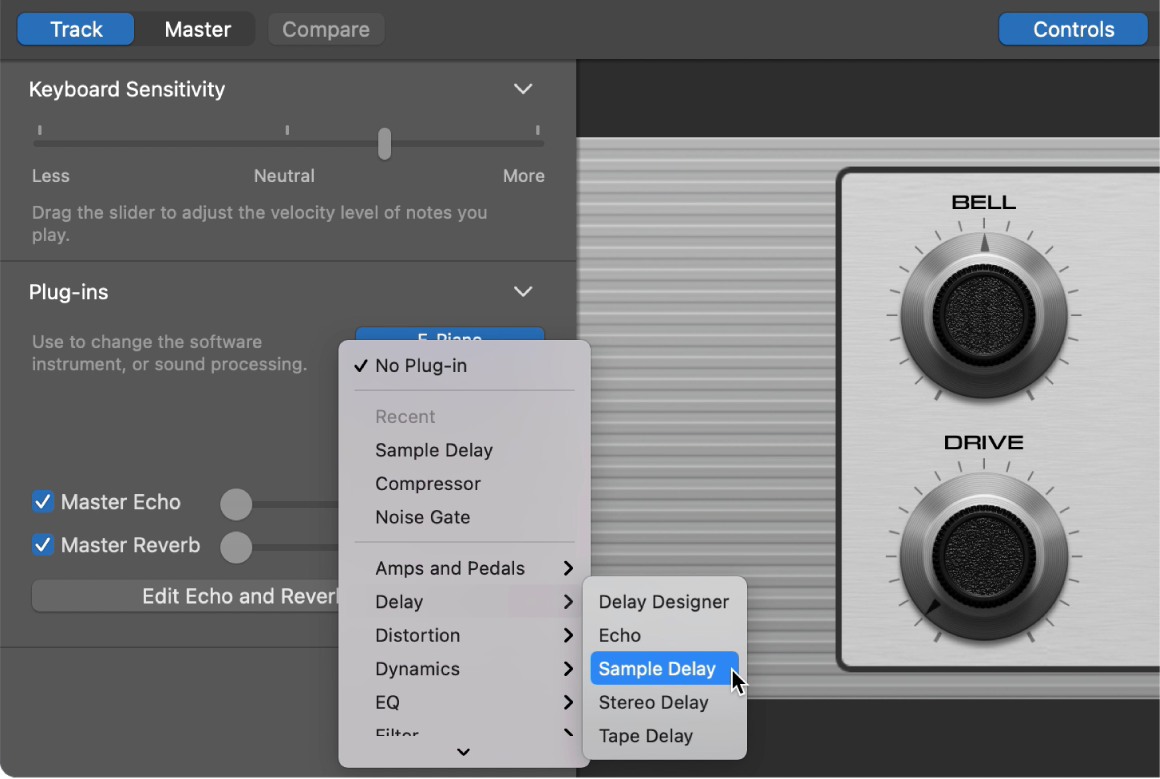
The plug-in window opens, showing the plug-in’s controls.
Choose a different plug-in
In GarageBand on Mac, click the right side of a plug-in slot, choose a category, then choose a new plug-in from the submenu. The new plug-in replaces the former selection.
Turn a plug-in off
In GarageBand on Mac, hold the pointer over the plug-in slot, then click the Power button on the left side of the plug-in slot.
Click the Power button again to turn the plug-in on.
Reorder effect plug-ins
In GarageBand on Mac, drag plug-ins by the center up or down.
Reordering plug-ins can change the sound of a patch. Plug-ins work in sequence; the output of a higher plug-in is sent to the input of the plug-in below it.
Remove an effect plug-in
In GarageBand on Mac, click the right side of a plug-in slot, then choose No Plug-in from the pop-up menu.
Edit plug-in settings
In GarageBand on Mac, click the center part of a plug-in slot to open the plug-in window.
In the plug-in window, drag sliders, move control points, and manipulate other controls to change the values of the effect settings.
Use the noise gate on an audio track
To turn the noise gate on or off: Select the Noise Gate checkbox.
Selecting the checkbox the first time adds the Noise Gate plug-in to the first effect slot in the Plug-ins area.
To adjust the sensitivity of the noise gate: Drag the Noise Gate slider left or right.
You can also use Audio Units plug-ins in your GarageBand projects to add new sounds and effects. For more information, see Use Audio Units plug-ins with GarageBand on Mac.