Denoiser controls in Final Cut Pro
Denoiser offers the following controls.
For information about adding the Denoiser effect to a clip and showing the effect’s controls, see Add Logic effects to clips in Final Cut Pro.
Main controls
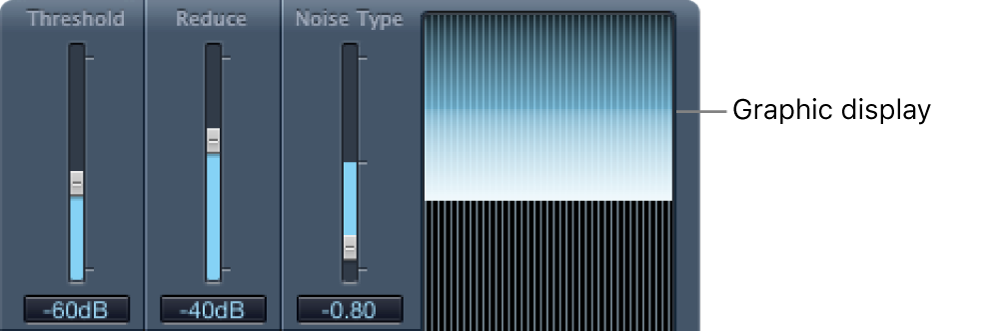
Threshold slider and field: Set the threshold level. Signals that fall below this level are reduced by Denoiser.
Reduce slider and field: Set the amount of noise reduction applied to signals that fall below the threshold. When reducing noise, remember that each 6 dB reduction is equivalent to halving the volume level (and each 6 dB increase is equivalent to doubling the volume level).
Note: If the noise floor of your recording is very high (more than −68 dB), reducing it to a level of −83 to −78 dB should be sufficient, provided this doesn’t introduce any audible side effects. This effectively reduces the noise by more than 10 dB, to less than half of the original (noise) volume.
Noise Type slider and field: Determine the type of noise that you want to reduce.
A value of 0 equals white noise (equal frequency distribution).
Positive values change the noise type to pink noise (harmonic noise; greater bass response).
Negative values change the noise type to blue noise (hissy tape noise).
Graphic display: Shows how the lowest volume levels of your audio material—which should be mostly, or entirely, noise—are reduced. Changes to parameters are instantly reflected here.
Smoothing controls
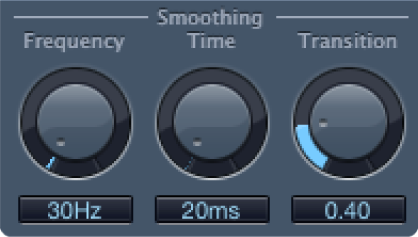
Frequency knob and field: Adjust how smoothing is applied to neighboring frequencies. If Denoiser recognizes that only noise is present on a certain frequency band, the higher you set the Frequency parameter, the more it changes the neighboring frequency bands to avoid glass noise.
Time knob and field: Set the time required by Denoiser to reach (or release) maximum reduction. This is the simplest form of smoothing.
Transition knob and field: Adjust how smoothing is applied to neighboring volume levels. If Denoiser recognizes that only noise is present in a certain volume range, the higher you set the Transition parameter, the more similar-level values are changed, in order to avoid glass noise.