Logic Pro User Guide for iPad
- What’s new in Logic Pro 1.1
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Working areas
- Work with function buttons
- Work with numeric values
-
- Intro to tracks
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Choose the default region type for a software instrument track
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Reorder tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Use the tuner on an audio track
- Show the output track in the Tracks area
- Delete tracks
- Edit track parameters
- Start a Logic Pro subscription
- How to get help
-
- Intro to recording
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Merge software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Capture your most recent MIDI performance
- Use the metronome
- Use the count-in
-
- Intro to arranging
-
- Intro to regions
- Select regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Remove gaps between regions
- Delay region playback
- Trim regions
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Mute regions
- Split and join regions
- Stretch regions
- Separate a MIDI region by note pitch
- Bounce regions in place
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Convert a MIDI region to a Drummer region or a pattern region
- Rename regions
- Change the color of regions
- Delete regions
- Create fades on audio regions
- Access mixing functions using the Fader
-
- Intro to Step Sequencer
- Use Step Sequencer with Drum Machine Designer
- Record Step Sequencer patterns live
- Step record Step Sequencer patterns
- Load and save patterns
- Modify pattern playback
- Edit steps
- Edit rows
- Edit Step Sequencer pattern, row, and step settings in the inspector
- Customize Step Sequencer
-
- Effect plug-ins overview
-
- Instrument plug-ins overview
-
- ES2 overview
- Interface overview
-
- Modulation overview
-
- Vector Envelope overview
- Use Vector Envelope points
- Use Vector Envelope solo and sustain points
- Set Vector Envelope segment times
- Vector Envelope XY pad controls
- Vector Envelope Actions menu
- Vector Envelope loop controls
- Vector Envelope release phase behavior
- Vector Envelope point transition shapes
- Use Vector Envelope time scaling
- Use the Mod Pad
- Modulation source reference
- Via modulation source reference
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Save a preset
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Low and highpass filter
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
- Sampler
- Copyright
ES1 filter parameters in Logic Pro for iPad
This section outlines the ES1 filter parameters.
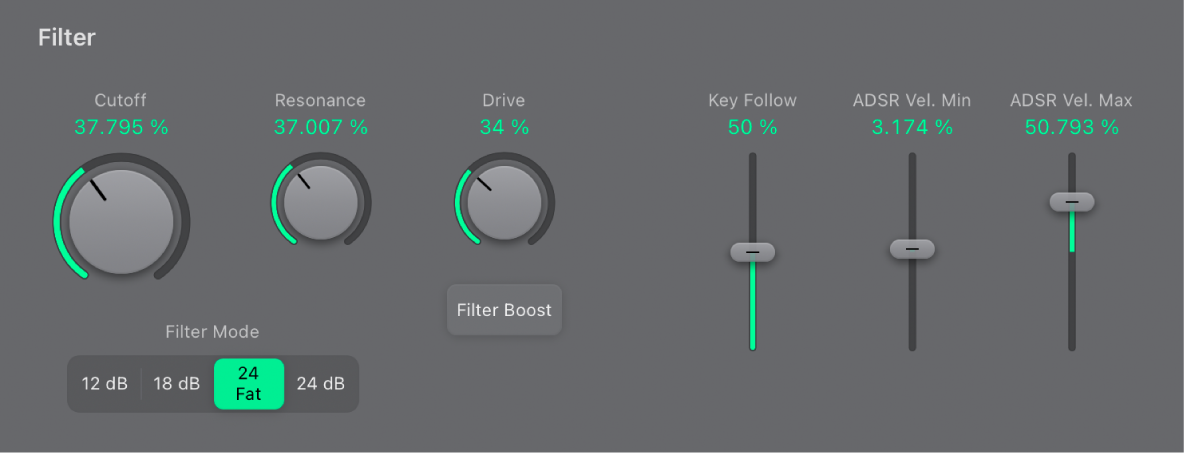
Filter parameters
 Cutoff knob and field: Set the cutoff frequency of the lowpass filter.
Cutoff knob and field: Set the cutoff frequency of the lowpass filter. Resonance knob and field: Cut or boost the portions of the signal that surround the frequency defined by the Cutoff parameter. Boost can be set so intensively that the filter begins to oscillate by itself.
Resonance knob and field: Cut or boost the portions of the signal that surround the frequency defined by the Cutoff parameter. Boost can be set so intensively that the filter begins to oscillate by itself.Filter Mode buttons: The lowpass filter offers four different slopes of band rejection above the cutoff frequency. Tap one of the buttons to choose a slope (amount of rejection, expressed in decibels (dB) per octave):
12 dB: Provides a soft, smooth sound that is reminiscent of the early Oberheim SEM synthesizer.
18 dB: Resembles the filter sound of the Roland TB-303.
24 Fat: Compensates for the reduction of low frequency content caused by high Resonance values. This resembles the behavior of an Oberheim filter.
24 dB: Mimics the behavior of a Moog filter. Increase the Resonance parameter value to reduce the low end of the signal.
Drive knob and field: Change the behavior of the Resonance parameter, which eventually distorts the sound of the waveform. Drive is actually an input level control, which allows you to overdrive the filter.
Filter Boost button: Increase the output of the filter by approximately 10 decibels. The filter input has a corresponding decrease of approximately 10 decibels, maintaining the overall level. This parameter is particularly useful when applying high Resonance values.
Key Follow slider and field: Set the effect that keyboard pitch (the note number) has on filter cutoff frequency modulation.
If Key Follow is set to zero, the cutoff frequency does not change, no matter which key you strike. This makes the lower notes sound comparatively brighter than higher notes.
If Key Follow is set to maximum, the filter follows the pitch, resulting in a constant relationship between cutoff frequency and pitch. This mirrors the properties of many acoustic instruments, where higher notes sound both brighter in tone and higher in pitch.
ADSR Vel Min/Max sliders and fields: Determine how note velocity affects modulation of the filter cutoff frequency with the envelope generator. Use the sliders to set minimum and maximum velocity range values. The greater the distance between the sliders, the more filter cutoff is affected by incoming velocity messages. See ES1 envelope parameters.
Output a sine wave from the filter
If you increase the filter Resonance parameter to higher values, the filter begins to internally feed back and, as a consequence, begins to self-oscillate. This results in a sine oscillation—a sine wave—that is actually audible.
You can make the ES1 filter output a sine wave by following the steps below. This lets you play the filter-generated sine wave with the keyboard.
In Logic Pro, switch the Sub Osc Wave knob to Off.
Drag the Osc Mix slider to the very bottom (Sub).
Set the Resonance knob to the maximum position.
If you wish, tap the Filter Boost button.
Filter Boost increases the output of the filter by approximately 10 decibels, making the self-oscillation signal much louder.
Play notes on your MIDI keyboard or the onscreen keyboard.
Control filter cutoff with velocity
The envelope generator modulates the filter cutoff frequency over the course of a note duration. The modulation intensity and response to velocity information is set with the ADSR Vel Min/Max sliders. The envelope generator also controls the level of the sound over time.
In the Logic Pro ES1 Filter section, set the minimum and maximum amount of modulation with the ADSR Vel Min/Max sliders and fields.
The difference between the ADSR Vel Min/Max sliders indicates the dynamic range of this modulation.
Set the ADSR sliders to the values you want to use, and adjust the ADSR Vel Min/Max sliders as needed.
Tip: If you’re unfamiliar with these parameters, set the Cutoff parameter to a low value, Resonance to a high value, and move both ADSR Vel Min/Max sliders upward. Constantly strike a note on the keyboard while changing the sliders to learn how these parameters work.
Download this guide: PDF