
View 360° video metadata using Compressor
For 360° video to display correctly on viewing devices and on sharing websites, the movie file must contain special display instructions called spatial metadata. Compressor handles that metadata in two ways:
On import: When you add a 360° video source file to Compressor, the app detects any spatial metadata present in the file and displays that information in the Job inspector. If the source video has no 360° metadata or if that metadata is incorrect, you can assign it yourself in the Job inspector.
On export: After you apply a transcode preset to the source file, Compressor assigns the correct metadata format for the export file. If necessary, you can modify this assignment in the Video inspector.
View or modify the source clip’s 360° metadata
After you add a 360° video source file to Compressor, make sure its metadata is correct.
In the Compressor batch area, select the source file.
In the Job inspector, review the properties shown in the 360° Metadata area.
If the 360° Metadata area is collapsed, move the pointer to the right of the heading, then click Show.
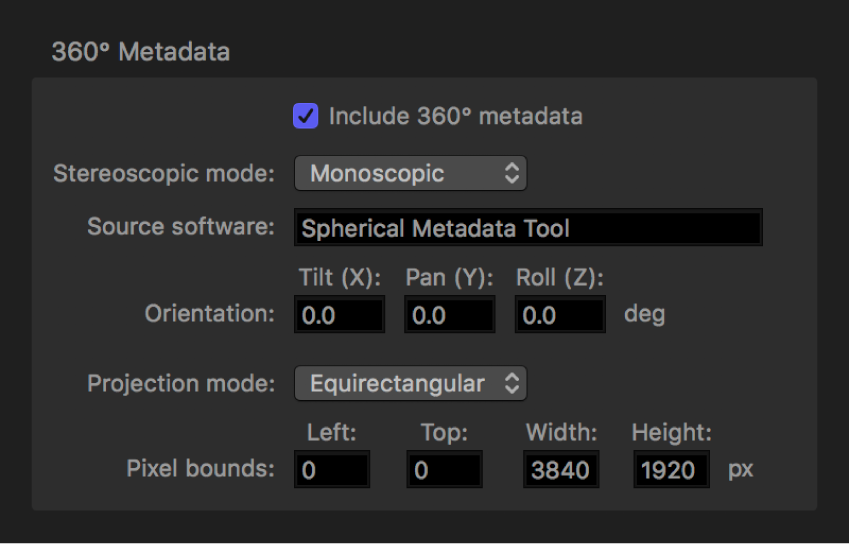
If necessary, add or modify metadata properties in the 360° Metadata area.
Note: If you modify properties in the 360° Metadata area, the image in the Compressor preview area stays the same. The preview area displays the 360° source file’s video with its native properties.
Include 360° metadata: Make sure this checkbox is selected. (If it’s not selected, the source file has no spatial metadata and you must add metadata yourself.)
Stereoscopic mode: Ensure that this pop-up menu is set to an appropriate option:
Monoscopic: Use this option for standard (2D) video.
Over/Under: Use this option for stereoscopic (3D) video that displays the left eye and right eye images vertically.
Side by Side: Use this option for stereoscopic (3D) video that displays the left eye and right eye images horizontally.
Source software: Identifies the software tool used to add metadata to the source file. If the source file had no metadata and you used Compressor to add it, this field displays “Apple CompressorKit.”
Orientation: Displays the coordinates—Tilt (X), Pan (Y), and Roll (Z), in degrees—of the source video’s view origin (the initial angle that viewers will see in a VR headset before they turn their heads). Enter new coordinates to change the initial orientation.
Projection mode: Sets the type of spatial mapping used to store the 360° video. There are two options:
Equirectangular: The most common form of spatial mapping for 360° video, this option squeezes and distorts the spherical data like a flat map of the world represents the surface of the spherical earth.
Cubic: A less common form of spatial mapping, this option represents the spherical data as an unfolded cube with six faces.

Pixel bounds: When “Projection mode” is set to Equirectangular, this property becomes available, allowing you to modify the boundaries of the equirectangular frame. Most of the time, there’s no need to change these values. However, if you need to alter the dimensions of 360° video from its 2:1 aspect ratio to a more conventional aspect ratio (16:9, for example), you can do so using these controls. Enter values in the Left and Top fields to crop a specific number of pixels from the left edge and top edge of the image. Enter new values in the Width and Height fields to change the dimensions of the equirectangular frame.
Layout and Padding: When “Projection mode” is set to Cubic, these fields become available, allowing you to adjust the six faces of the unfolded cube. Most of the time, there’s no need to change these values. The integer value in the Layout field specifies the order of the six unfolded cube faces (the default value of 0 specifies the face order used in the Spherical Video V2 metadata standard: right, left, up, down, front, back). The value in the Padding field specifies the width (in pixels) of borders around the edges of each cube face.
Include 360° metadata in the output file
After you apply a transcode preset to the 360° video source file, make sure the preset uses the correct metadata format for the output destination you’ve chosen (YouTube, Vimeo, or another publishing platform). In most cases, Compressor automatically chooses the correct metadata format for the job, based on the values entered in the Job inspector and the transcode preset you applied. However, you can modify that choice, if necessary.
In the Compressor batch area, select an applied preset.
In the Video inspector, click the “360° metadata” pop-up menu (in the Video Properties area) and choose an option:
Automatic: Compressor chooses the metadata format based on the properties in the Job inspector and the transcode preset you applied. The format chosen is listed to the right of the pop-up menu.
None: No 360° metadata is attached to your output file.
Spherical Video V1: The 360° metadata format most commonly used by sharing sites, including YouTube and Vimeo.
Spherical Video V2: A less common but more up-to-date 360° metadata format used by YouTube and Vimeo.
Click Start Batch to export your file and its 360° metadata.
If you applied a YouTube or Vimeo destination to the source file, the metadata will be parsed by the sharing website so that your 360° video displays correctly.
Download this guide: PDF