Logic Pro User Guide for iPad
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Working areas
- Work with function buttons
- Work with numeric values
-
- Intro to tracks
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Choose the default region type for a software instrument track
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Reorder tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Use the tuner on an audio track
- Show the output track in the Tracks area
- Delete tracks
- Edit track parameters
- Start a Logic Pro subscription
- How to get help
-
- Intro to recording
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Merge software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Capture your most recent MIDI performance
- Use the metronome
- Use the count-in
-
- Intro to arranging
-
- Intro to regions
- Select regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Remove gaps between regions
- Delay region playback
- Trim regions
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Mute regions
- Split and join regions
- Stretch regions
- Separate a MIDI region by note pitch
- Bounce regions in place
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Convert a MIDI region to a Drummer region or a pattern region
- Rename regions
- Change the color of regions
- Delete regions
- Create fades on audio regions
- Access mixing functions using the Fader
-
- Intro to Step Sequencer
- Use Step Sequencer with Drum Machine Designer
- Record Step Sequencer patterns live
- Step record Step Sequencer patterns
- Load and save patterns
- Modify pattern playback
- Edit steps
- Edit rows
- Edit Step Sequencer pattern, row, and step settings in the inspector
- Customize Step Sequencer
-
- Effect plug-ins overview
-
- Instrument plug-ins overview
-
- ES2 overview
- Interface overview
-
- Modulation overview
-
- Vector Envelope overview
- Use Vector Envelope points
- Use Vector Envelope solo and sustain points
- Set Vector Envelope segment times
- Vector Envelope XY pad controls
- Vector Envelope Actions menu
- Vector Envelope loop controls
- Vector Envelope release phase behavior
- Vector Envelope point transition shapes
- Use Vector Envelope time scaling
- Use the Mod Pad
- Modulation source reference
- Via modulation source reference
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Save a preset
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Low and Highpass filter
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
- Sampler
- Copyright
Space Designer Output EQ in Logic Pro for iPad
Space Designer has a six-band Output EQ consisting of high and low cut bands, two parametric mid-bands, plus a low shelving filter and a high shelving filter.
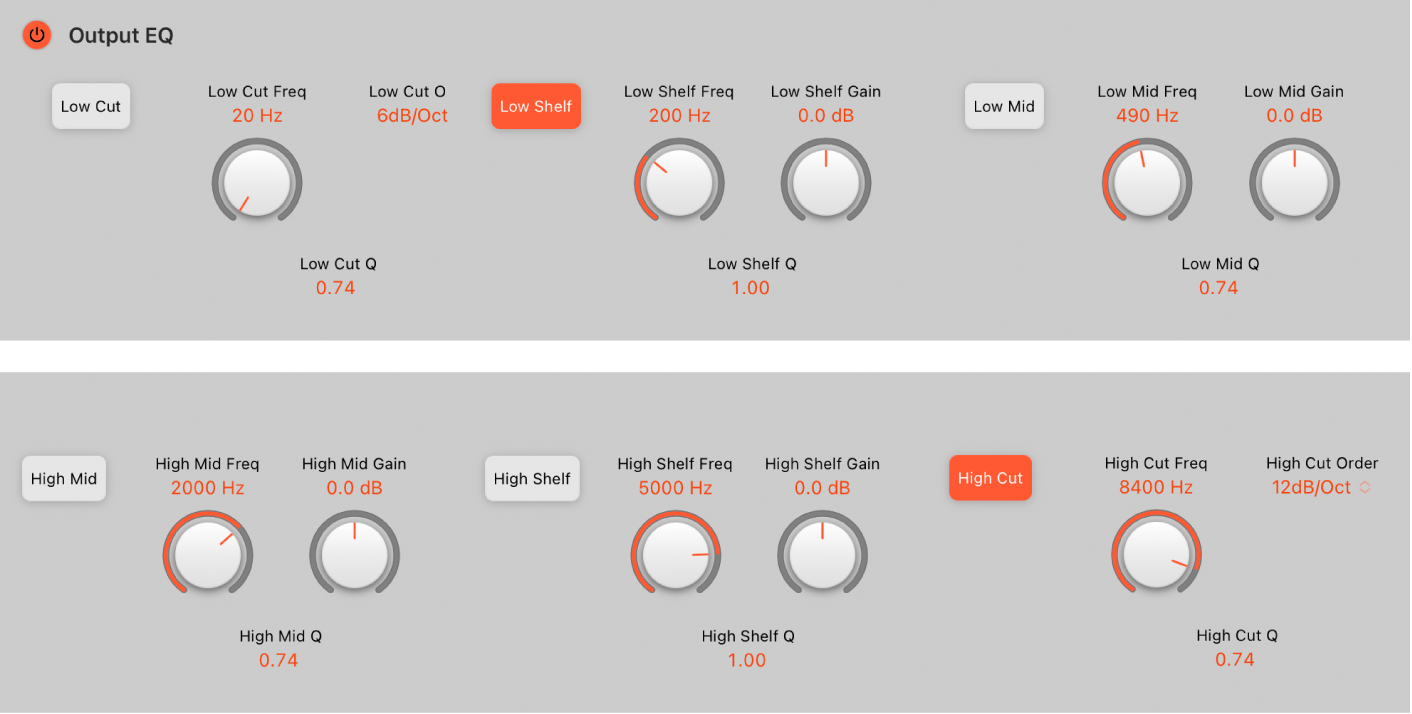
Output EQ parameters
Output EQ On/Off button: Turn on to enable the Output EQ, which adjusts frequencies of the overall combined reverb and source signal.
Low Cut button: Switch on a highpass filter that allows high frequencies to pass and reduces the level of low frequencies near the cutoff (set) frequency.
Low Cut Freq knob and field: Set the frequency for the Low Cut band.
Low Cut Order pop-up menu: Choose the filter rolloff amount for the Low Cut band. Higher order filters have a steeper rolloff.
Low Cut Q field: Set the Q factor—the width—for the Low Cut band. Low values result in a narrow frequency band selection. High values encompass a broad frequency band.
Low Shelf button: Switch on a low shelving filter that adjusts the level of low frequencies and has a minimal impact on frequencies above the cutoff (set) frequency.
Low Shelf Freq knob and field: Set the frequency for the Low Shelf band.
Low Shelf Gain knob and field: Cut or boost the Low Shelf band.
Low Shelf Q field: Set the Q factor—the width—for the Low Shelf band. Low values result in a narrow frequency band selection. High values encompass a broad frequency band.
Low Mid button: Switch on a parametric bell filter with three controls.
Low Mid Freq knob and field: Set the frequency for the Low Mid band.
Low Mid Gain knob and field: Cut or boost the Low Mid band.
Low Mid Q field: Set the Q factor—the width—for the Low Mid band. Low values result in a narrow frequency band selection. High values encompass a broad frequency band.
High Mid button: Switch on a parametric bell filter with three controls.
High Mid Freq knob and field: Set the frequency for the High Mid band.
High Mid Gain knob and field: Cut or boost the High Mid band.
High Mid Q field: Set the Q factor—the width—for the High Mid band. Low values result in a narrow frequency band selection. High values encompass a broad frequency band.
High Shelf button: Switch on a high shelving filter that adjusts the level of high frequencies and has a minimal impact on frequencies below the cutoff (set) frequency.
High Shelf Freq knob and field: Set the frequency for the High Shelf band.
High Shelf Gain knob and field: Cut or boost the High Shelf band.
High Shelf Q field: Set the Q factor—the width—for the High Shelf band. Low values result in a narrow frequency band selection. High values encompass a broad frequency band.
High Cut button: Switch on a lowpass filter that allows low frequencies to pass and reduces the level of high frequencies near the cutoff (set) frequency.
High Cut Freq knob and field: Set the frequency for the High Cut band.
High Cut Order pop-up menu: Choose the filter rolloff amount for the High Cut band. Higher order filters have a steeper rolloff.
High Cut Q field: Set the Q factor—the width—for the High Cut band. Low values result in a narrow frequency band selection. High values encompass a broad frequency band.
Download this guide: PDF