Logic Pro User Guide for Mac
- Welcome
-
- What’s new in Logic Pro for Mac 11.1
- What’s new in Logic Pro for Mac 11
- What’s new in Logic Pro for Mac 10.8
- What’s new in Logic Pro for Mac 10.7.8
- What’s new in Logic Pro for Mac 10.7.5
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.7.3
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.7
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.6
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.5
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.4
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.3
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.2
- What’s new in Logic Pro 10.0
-
- What is Logic Pro for Mac?
- Logic Pro project basics
- Use menu commands and key commands
- Use the complete set of Logic Pro features
- Undo and redo edits
- Manage Logic Pro content
- How to get help
-
- Projects overview
- Create projects
- Open projects
- Save projects
- Delete projects
-
- Play a project
- Set the playhead position
- Control playback with the transport buttons
- Use transport shortcut menus
- Use transport key commands
- Customize the control bar
- Change the LCD display mode in Logic Pro for Mac
- Monitor and reset MIDI events
- Use the cycle area
- Use the Chase Events function
- Use Apple Remote to control Logic Pro
- Use Logic Remote to control Logic Pro projects
- Preview projects in the Finder
- Close projects
- View project information
-
- Tracks overview
-
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Create tracks using existing channel strips
- Assign tracks to different channel strips
- Choose the default region type for software instrument tracks
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Reorder tracks
- Zoom tracks
- Replace or double drum sounds
- Control timing with the groove track
- Use selection-based processing
- Edit track parameters
-
- Overview
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Play software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Overdub software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Use Note Repeat
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Use step input recording techniques
- Record MIDI messages from another music app
- Route MIDI internally to software instrument tracks
- Use the metronome
-
- Arranging overview
-
- Regions overview
- Select regions
- Select parts of regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Add or remove gaps
- Delay region playback
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Resize regions
- Mute and solo regions
- Time stretch regions
- Reverse audio regions
- Split regions
- Demix MIDI regions
- Join regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Change the gain of audio regions in the Tracks area
- Normalize audio regions in the Tracks area
- Create aliases of MIDI regions
- Convert repeated MIDI regions to loops
- Change the color of regions
- Convert a MIDI region into a pattern region in Logic Pro for Mac
- Replace a MIDI region with a Session Player region in Logic Pro for Mac
- Convert audio regions to samples for a sampler instrument
- Rename regions
- Delete regions
-
- Chords overview
- Add and delete chords
- Select chords
- Cut, copy, and paste chords
- Move and resize chords
- Loop chords on the Chord track
- Transpose chords
- Edit chords
- Work with chord groups
- Use chord progressions
- Change the chord rhythm
- Choose which chords a Session Player region follows
- Analyze the key signature of a range of chords
- Extract vocal and instrumental stems with Stem Splitter
- Create groove templates
-
- Overview
-
- Add notes
- Select notes
- Snap items to the grid
- Move notes
- Copy notes
- Change the pitch of notes
- Resize notes
- Edit note velocity
- Quantize the timing of notes
- Quantize the pitch of notes
- Change note articulations
- Lock the position of events
- Mute notes
- Change note color
- View note labels
- Delete notes
- Time stretch notes
- View multiple MIDI regions
- Split chords
- Automation/MIDI area in the Piano Roll Editor
- Open other editors
-
- Session Players overview
- The Session Player Editor
- Choose a Session Player type and style
- Chords and Session Players
- Choose Session Player presets
- Regenerate a Session Player performance
- Follow rhythm of chords and other tracks
- Work with Drummer multi-channel kits
- Convert Session Player regions into MIDI or pattern regions
-
- Logic Pro for Mac advanced editors overview
-
- Audio File Editor overview
- Play audio files in the Audio File Editor
- Navigate audio files in the Audio File Editor
-
- Audio File Editor edit commands
- Edit audio files with transient markers
- Use the Audio File Editor Pencil tool
- Trim or silence audio files
- Remove DC offset
- Set audio file levels
- Normalize audio files
- Fade audio files
- Reverse audio and invert phase
- Audio File Editor Loop commands
- Undo Audio File Editor edits
- Backup audio files
- Use an external sample editor
-
- Mixing overview
- Set channel strip input format
- Set channel strip pan or balance positions
- Mute and solo channel strips
- Reorder channel strips in the Mixer
-
- Plug-ins overview
- Add, remove, move, and copy plug-ins
- Search for plug-ins in the Mixer
- Insert a plug-in on a track using drag and drop
- Activate plug-ins on inactive channel strips
- Use the Channel EQ
- Work in the plug-in window
- Work with plug-in settings
- Work with plug-in latencies
- Work with Audio Units in Logic Pro for Mac
- Support for ARA 2 compatible plug-ins
- Use MPE with software instruments
- Use the Plug-in Manager
- Work with channel strip settings
- Surround panning
- Use the I/O Labels window
- Undo and redo Mixer and plug-in adjustments
-
- Smart Controls overview
- Show Smart Controls for master effects
- Choose a Smart Control layout
- Automatic MIDI controller assignment
- Map screen controls automatically
- Map screen controls
- Edit mapping parameters
- Use parameter mapping graphs
- Open the plug-in window for a screen control
- Rename a screen control
- Use articulation IDs to change articulations
- Assign hardware controls to screen controls
- Compare Smart Control edits with saved settings
- Use the Arpeggiator
- Automate screen control movements
-
- Live Loops overview
- Start and stop cells
- Work with Live Loops cells
- Change loop settings for cells
- How the Live Loops grid and Tracks area interact
- Edit cells
- Edit scenes
- Work in the Cell Editor
- Bounce cells
- Record a Live Loops performance
- Change Live Loops grid settings
- Control Live Loops with other devices
-
- Global changes overview
- Control transposition with the Pitch Source parameter
-
- Tempo overview
-
- Smart Tempo overview
- Use free tempo recording
- Choose the Project Tempo mode
- Choose the Flex & Follow setting
- Use Smart Tempo with multitrack audio
- Work in the Smart Tempo Editor
- Improve the tempo analysis using hints
- Correct tempo analysis results using beat markers
- Protect Smart Tempo edits by locking a range
- Match audio recordings to the project tempo
- Match the tempo to an audio region
- Use audio file tempo information
- Record tempo changes
- Use the Tempo Interpreter
- Use the tempo fader
- Control project volume
-
- Overview
- Add notes
-
- Part box overview
- View score symbols
- Select score symbols
- Add notes and rests
- Add notes and symbols to multiple regions
- Add key and time signature changes
- Change the clef sign
- Add dynamic marks, slurs, and crescendi
- Change note heads
- Add symbols to notes
- Add trills, ornaments, and tremolo symbols
- Add sustain pedal markings
- Add chord symbols
- Add chord grids and tablature symbols
- Add bar lines, repeats, and coda signs
- Add page and line break symbols
-
- Select notes
- Move and copy notes
- Change note pitch, duration, and velocity
- Change note articulations
- Quantize the timing of notes
- Restrict note input to the current key
- Control how ties are displayed
- Add and edit tuplets
- Override display quantization using tuplets
- Add grace notes and independent notes
- Delete notes
- Use automation in the Score Editor
-
- Staff styles overview
- Assign staff styles to tracks
- Staff Style window
- Create and duplicate staff styles
- Edit staff styles
- Edit staff, voice, and assign parameters
- Add and delete staffs or voices in the Staff Style window in Logic Pro for Mac
- Copy staffs or voices in the Staff Style window in Logic Pro for Mac
- Copy staff styles between projects
- Delete staff styles
- Assign notes to voices and staffs
- Display polyphonic parts on separate staffs
- Change the staff assignment of score symbols
- Beam notes across staffs
- Use mapped staff styles for drum notation
- Predefined staff styles
- Share a score
-
-
- Key commands overview
- Browse, import, and save key commands
- Assign key commands
- Copy and print key commands
-
- Global Commands
- Global Control Surfaces Commands
- Various Windows
- Windows Showing Audio Files
- Main Window Tracks and Various Editors
- Various Editors
- Views Showing Time Ruler
- Views Showing Automation
- Main Window Tracks
- Live Loops Grid
- Mixer
- MIDI Environment
- Piano Roll
- Score Editor
- Event Editor
- Step Editor
- Step Sequencer
- Project Audio
- Audio File Editor
- Smart Tempo Editor
- Library
- Sampler
- Drum Machine Designer
- Step Input Keyboard
- Smart Controls
- Tool Menu
- Control Surface Install Window
-
- Logic Pro projects
- Various windows
- Controller Assignments window
- Control bar
- Tracks area
- Global tracks
- Automation
- Live Loops grid
- Mixer
- MIDI Environment
- Piano Roll Editor
- Score Editor
- Event List
- Step Editor
- Step Sequencer
- Flex Time
- Audio File Editor
- Smart Tempo Editor
- Surround Panner
- Channel EQ
- Space Designer
- Sampler
- Touch Bar shortcuts
-
-
- Working with your control surface
- Connect control surfaces
- Add a control surface to Logic Pro for Mac
- Automatic assignment for USB MIDI controllers
- Grouping control surfaces
- Control Surfaces settings overview
- Modal dialog display
- Tips for using your control surface
- Supported control surfaces
- Software and firmware for Logic Pro for Mac
-
-
- Environment overview
- Common object parameters
- Customize the Environment
-
-
- Fader objects overview
- Use fader objects
- Play back fader movements
- Work with object groups
- Fader styles
- Fader functions: MIDI events
- Fader functions: range, value as
- Fader functions: filter
- Vector fader
- Special faders overview
- Cable switchers
- Meta event faders
- SysEx faders
- Work with SysEx messages
- Special functions
- Ornament objects
- MMC record buttons
- Keyboard objects
- Monitor objects
- Channel splitter object
- Physical input objects
- Physical input objects
- MIDI click objects
-
-
- Use MIDI plug-ins
-
- Arpeggiator overview
- Arpeggiator control parameters
- Note order parameters overview
- Note order variations
- Note order inversions
- Arpeggiator pattern parameters overview
- Use Live mode
- Use Grid mode
- Arpeggiator options parameters
- Arpeggiator keyboard parameters
- Use keyboard parameters
- Assign controllers
- Modifier controls
- Note Repeater controls
- Randomizer controls
-
- Use Scripter
- Use the Script Editor
- Scripter API overview
- MIDI processing functions overview
- HandleMIDI function
- ProcessMIDI function
- GetParameter function
- SetParameter function
- ParameterChanged function
- Reset function
- JavaScript objects overview
- Use the JavaScript Event object
- Use the JavaScript TimingInfo object
- Use the Trace object
- Use the MIDI event beatPos property
- Use the JavaScript MIDI object
- Create Scripter controls
- Transposer controls
- Record MIDI to Track
-
-
- Alchemy overview
- Alchemy interface overview
- Alchemy Name bar
- Alchemy file locations
-
- Alchemy source overview
- Source master controls
- Import browser
- Source subpage controls
- Source filter controls
- Source filter use tips
- Source elements overview
- Additive element controls
- Additive element effects
- Spectral element controls
- Spectral element effects
- Pitch correction controls
- Formant filter controls
- Granular element controls
- Sampler element controls
- VA element controls
- Wide unison mode
- Source modulations
- Morph controls
- Alchemy master voice section
- Alchemy Extended parameters
-
- ES2 overview
- ES2 interface overview
- ES2 integrated effects processor controls
- Use ES2 in Surround mode
- Extended parameters
-
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Lowpass, bandpass, and highpass filters
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
-
- Sculpture overview
- Sculpture interface
- Global parameters
- Amplitude envelope parameters
- Use the Waveshaper
- Filter parameters
- Output parameters
- Use surround range and diversity
- Define MIDI controllers
- Extended parameters
-
- Studio Piano
-
- Ultrabeat overview
- Ultrabeat interface
- Synthesizer section overview
- Filter section controls
- Distortion circuit controls
- Glossary
- Copyright

ChromaGlow in Logic Pro for Mac
ChromaGlow is a saturation plug-in designed to replicate the warmth and coloration of analog audio equipment. By introducing harmonic distortion to incoming audio signals, it emulates the nonlinear response and subtle compression found in analog gear. This process enriches the harmonic content of the audio, resulting in a more nuanced and textured sound with enhanced character and depth. Additionally, the subtle compression effect helps to smooth out dynamics and tame transients, contributing to a polished and professional-sounding end result.
ChromaGlow is available on Macs with an M1 or later Apple silicon processor.
To add ChromaGlow to your project, choose Distortion > ChromaGlow in a channel strip Audio Effect plug-in menu. See Add, remove, move, and copy plug-ins in Logic Pro for Mac.
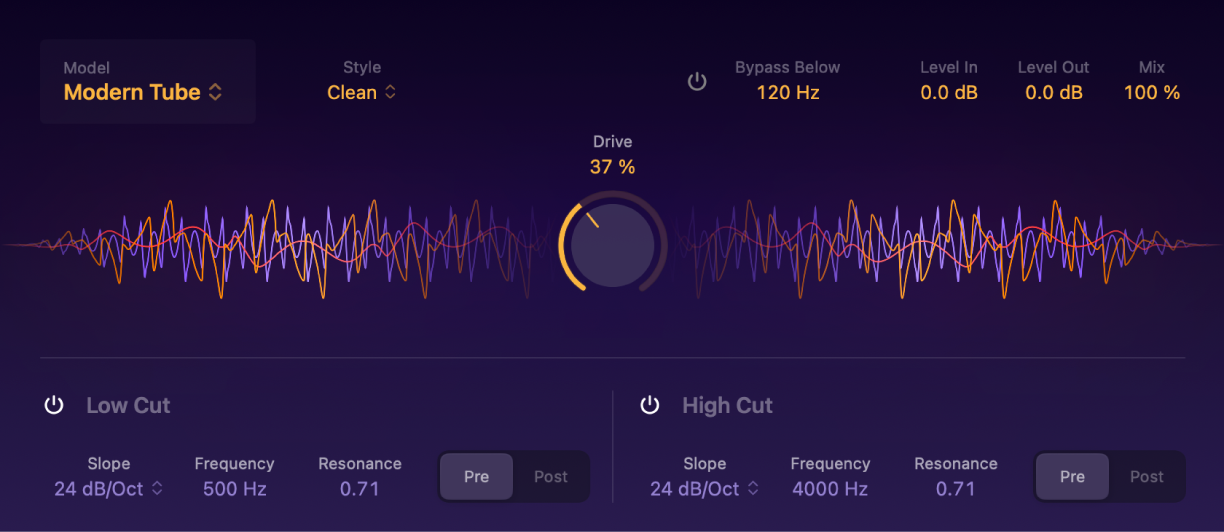
ChromaGlow parameters
Model pop-up menu: Choose from a range of saturation models that emulate vintage audio equipment.
Retro Tube: Replicates the warmth and even-order harmonics characteristic of vacuum tube equipment, offering a smooth and pleasant distortion that infuses audio with warmth and a vintage ambiance.
Modern Tube: Imparts the harmonic richness, gentle compression, and pleasing distortion that is typical of tube-based gear. This type of saturation can add warmth, character, and a vintage vibe to audio signals, making it a popular choice for enhancing the sound of individual tracks or entire mixes.
Magnetic: Mimics the saturation and compression qualities of analog tape machines. It introduces a warm, organic, and slightly compressed sound, with added harmonics. It’s great for achieving a vintage, analog feel.
Squeeze: Replicates the saturation achieved through intentional pushing of a compressor, which introduces harmonic distortion and modifies the tonal characteristics of an audio signal. This imparts warmth, character, and color to the sound.
Analog Preamp: Provides an assertive, vibrant, and punchy sound characterized by a distinctively sharp and edgy quality, in contrast to the smoother distortion of tubes or the gentle saturation of tape.
Style pop-up menu: Choose an alternative style for the selected model to impart a different colorization to the sound.
Retro Tube: When selected, the following styles are available:
Clean: Subtly and smoothly adds a touch of warmth to the sound along with a slight muddiness.
Colorful: Introduces a significant amount of character to the sound while also imparting a noticeable sense of muddiness.
Modern Tube: When selected, the following styles are available:
Clean: Delivers a pristine and transparent sound with a touch of warmth. It preserves the clarity of the audio while subtly enhancing it with the characteristics typically associated with tube amplification.
Colorful: Blends classic warmth with modern clarity, offering rich, harmonically nuanced audio reminiscent of vintage amps, but with with improved fidelity.
Magnetic: When selected, the following styles are available:
Colorful: Turns on the transformer component to deliver a saturated, warm, and character-rich sound.
Clean: Turns off the transformer component for a cleaner signal with less harmonic content.
Squeeze: When selected, the following styles are available:
Soft Press: Delivers smooth, natural compression with gentle characteristics, enhancing warmth and richness. This option is ideal for achieving subtle, musical compression.
Hard Press: Generates assertive, punchy compression with evident distortion. Use this style for a more dramatic impact, particularly on percussive sounds, or to attain a pronounced and bold vocal presence.
Analog Preamp: When selected, the following styles are available:
Clean: Turns on a transistor-based saturation circuit, resulting in a cleaner signal with reduced distortion.
Colorful: Provides a vintage, woolly sound with soft clipping, offering a subtly compressed and warm tone.
Drive knob and field: Set the amount of saturation applied to the signal.
Bypass Below button: Turn the Bypass Below control on or off.
Bypass Below field: Set the frequency threshold below which the effect is bypassed. Frequencies below this threshold will remain unaffected, while the effect is applied to frequencies above it.
Level In field: Set the amount of gain applied to the plug-in input signal.
Level Out field: Set the amount of gain applied to the plug-in output signal.
Mix field: Set the percentage of the effect signal mixed with the original signal.
Display: Shows the intensity of the saturation settings on the signal.
Low Cut parameters
Low Cut button: Turn the low cut filter on or off.
Slope pop-up menu: Choose a slope to determine the extent of frequency reduction. Increasing the slope to a higher number results in more extreme filtering.
Frequency field: Set the cutoff frequency of the lowpass filter.
Resonance field: Set to emphasize frequencies surrounding the cutoff frequency.
Pre/Post buttons: Apply low cut equalization adjustments to the audio signal before or after the saturation effect is applied.
High Cut parameters
High Cut button: Turn the high cut filter on or off.
Slope pop-up menu: Choose a slope to determine the extent of frequency reduction. Increasing the slope to a higher number results in more extreme filtering.
Frequency field: Set the cutoff frequency of the highpass filter.
Resonance field: Set to emphasize frequencies surrounding the cutoff frequency.
Pre/Post buttons: Apply high cut equalization adjustments to the audio signal before or after the saturation effect is applied.