
Properties Inspector controls in Motion
The Properties Inspector displays the adjustable parameters for most layers and groups. Available parameters may change depending on the currently selected object.
Important: The Transform, Cast Reflections, Four Corner, Crop, Lighting, Shadow, and Reflection parameters are not available for layers within 360° environments. Only basic Blending, Drop Shadow, and Timing parameters are available for 360° environments.
Transform parameters
Position: Value sliders that define the X (horizontal), Y (vertical), and Z (depth) positions of each layer.
Click the disclosure triangle next to the Position parameter to reveal dials that adjust position around all three axes (X, Y, and Z).
The coordinate system used by Motion specifies the center of the canvas as 0, 0, 0 regardless of the frame size of the project. Moving a layer to the left subtracts from the X value, while moving it to the right adds to the X value. Moving a layer up adds to the Y value, and moving a layer down subtracts from the Y value. Moving a layer closer adds to the Z value, while moving a layer farther away subtracts from the Z value.
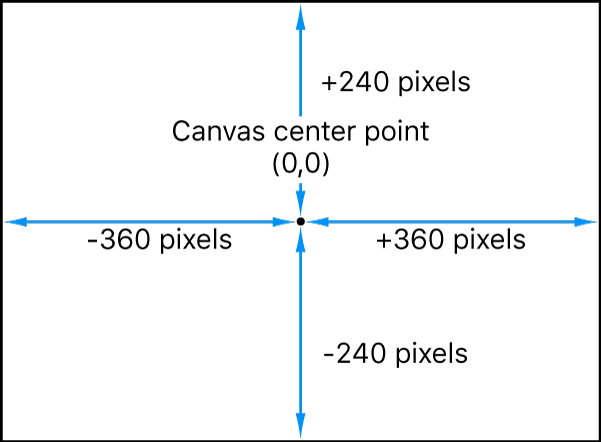
Each layer’s position is centered on its anchor point. Offsetting the anchor point also offsets the position of the layer relative to the X, Y, and Z position values you’ve set.
Rotation: A dial that controls a one-dimensional value representing the number of degrees of rotation around the Z axis. A positive value rotates the layer counterclockwise; a negative value rotates the layer clockwise. Rotating a layer beyond 360 degrees results in multiple rotations when the Rotation parameter is animated.
Click the disclosure triangle next to the Rotation parameter to reveal dials that adjust rotation around all three axes (X, Y, and Z), as well as the Animate pop-up menu.
Animate: A pop-up menu that sets the interpolation for animated 3D rotation channels to one of two options:
Use Rotation: The default interpolation method. Layer rotates from its start angle to its final angle. Depending on the animation, the layer might twist before reaching its final orientation (the last keyframed value). For example, if the X, Y, and Z Angle parameters are animated from 0 degrees to 180 degrees in a project, the layer rotates on all axes before reaching its final orientation.
Use Orientation: This alternate interpolation method provides smoother interpolation but does not allow multiple revolutions. Use Orientation interpolates between the layer’s start orientation (first keyframe) to its end orientation (second keyframe).
Note: The Rotation parameter must be keyframed for its Animate parameter options to have any effect. For information about keyframing, see Intro to keyframing in Motion. For information about 3D rotation, see Transform layers in 3D space in Motion.
Scale: A slider that controls the layer’s scale, relative to its original size. By default, the horizontal and vertical scale of a layer is locked to the layer’s original aspect ratio—represented by a single percentage. Click the disclosure triangle to display independent percentages for the X, Y, and Z scales of the layer.
Note: Setting a layer’s scale to a negative value flips the layer.
Shear: Value sliders that define the X and Y shear of the layer. A layer with no shear has X and Y shear values of 0. Positive values shear in one direction, while negative values shear in the other.
Anchor Point: Value sliders that define the X and Y position of the anchor point relative to the center of the layer. Coordinates of 0, 0 center the anchor point in the bounding box defining the outer edge of the layer. Click the disclosure triangle to expose an additional value slider defining the Z position.
Blending parameters
Opacity: A slider that sets the transparency of the layer. See Modify layer opacity in Motion.
Blend Mode: A pop-up menu that sets the Blend Mode of the layer. See Intro to layer blending in Motion.
Preserve Opacity: A checkbox that, when selected, renders the layer visible only where another layer is visible behind it in the composite. The front layer uses the opacity value of the layer behind it. See Modify layer opacity in Motion.
Casts Reflections: A pop-up menu that determines whether a layer casts a reflection. Choose from three options:
Yes: The layer is seen reflected in nearby reflective layers.
No: The layer is ignored by reflective surfaces.
Reflection Only: The layer becomes invisible, but appears in reflective surfaces around it.
Note: Reflections are only visible when layers are in a 3D group. For more information on 3D groups, see 2D and 3D group properties in Motion.
Color parameters
In a project with Color Processing set to Automatic, additional color management controls become available when you select an image or clip in the Layers list.
Conversion: A pop-up menu that sets the media’s color conversion type. Choose from two options:
Automatic: Lets Motion determine the conversion type (based on the media and the Render Color Space setting in the View pull-down menu).
Manual: Displays the Conversion Type pop-up menu, with options to choose a conversion type other than the default.
Important: In most cases, manually converting an image or clip is unnecessary—Automatic will choose the best conversion type for all media in the project, adjusting the dynamic range of an image or clip to better match the project’s Render Color Space setting (in the View pull-down menu).
Conversion Type: A pop-up menu (available only when Manual is chosen from the Conversion pop-up menu) that converts a clip from one color space to another using tone mapping. Choose from five options:
To/From 100% HDR (HLG): Converts a clip to or from 100% of the HDR HLG dynamic range whenever the clip needs to be tone mapped. For example, if the Render Color Space is set to Rec. 709, the full dynamic range of HLG is tone mapped to the full (but more limited) dynamic range of SDR, resulting in an HLG image that appears correct in the project. If the Render Color Space is set to HDR Rec. 2020 HLG, the full (but limited) dynamic range of Rec. 709 is inverse tone mapped to the full dynamic range of HLG. (If the clip is HLG and the render color space is set to HDR Rec. 2020 HLG, then no conversion occurs.)
In general, use this option when your SDR media needs to expand to the maximum dynamic range of HLG HDR, or when HLG media contains HDR-level brightness (brighter than SDR media).
(This is the default conversion type applied to HLG media when the Conversion pop-up menu is set to Automatic.)
To/From 75% HDR (HLG): Converts a clip to or from 75% of the HDR HLG dynamic range whenever the clip needs to be tone mapped. For example, if the Render Color Space is set to Rec. 709, 75% of the dynamic range of HLG is tone mapped to the full (but more limited) dynamic range of SDR. If the Render Color Space is set to HDR Rec. 2020 HLG, the full (but limited) dynamic range of SDR is tone mapped to 75% of the dynamic range of HLG. (If the clip is HLG and Render Color Space is set to HDR Rec. 2020 HLG, then no conversion occurs.)
In general, use this option to keep SDR media at SDR-level brightness when used in an HDR HLG project, or when HLG media doesn’t contain HDR-level brightness (such as an SDR clip that’s recorded and encoded as HLG).
To/From HDR (PQ): Converts a clip to or from HDR PQ based on the project’s current render color space. For example, when the render color space is set to HDR Rec. 2020 HLG, a PQ clip is converted from PQ to HLG so it appears correct in the project.
When this option is selected, the PQ Peak (nits) slider becomes available in the clip’s Properties Inspector, letting you adjust the peak brightness (nits value) of a PQ clip. The PQ Peak (nits) value is the default value of the PQ clip (1,000 nits, or the value of any peak mastering metadata in the clip).
(This is the default conversion type for PQ media when the Conversion pop-up menu is set to Automatic.)
Use HDR White Level (75%): Instructs an image or clip to use the HDR White Level slider (in the Project Properties Inspector) to adjust its brightness. If you’ve previously changed the default value of the HDR White Level slider in the Project Properties Inspector, that value is displayed in the pop-up menu.
(This is the default conversion type for SDR media when the Conversion pop-up menu is set to Automatic.)
None: No conversion occurs.
For more information, see Manage automatic color processing in Motion.
Drop Shadow parameters
An activation checkbox that turns the drop shadow of a layer on and off. When selected, additional controls become available:
Color: Color controls that set the drop shadow’s color. The default color is black.
Opacity: A slider that sets the drop shadow’s transparency.
Blur: A slider that specifies the drop shadow’s softness.
Distance: A slider that sets how close or far a layer’s drop shadow is to the layer. The farther away a drop shadow is, the more distance there appears to be between the layer and anything behind it in the composition.
Angle: A dial that lets you change the direction of the drop shadow. Changing the Angle of the drop shadow changes the apparent direction of the light casting the shadow.
Fixed Source: A checkbox that, when selected, renders the drop shadow as if cast by a fixed light source, regardless of camera or text movement.
Four Corner parameters
An activation checkbox that turns distorting on and off. If a layer is distorted and this checkbox is deselected, the layer resumes its original shape, although the distorted coordinates are maintained. Reselecting the checkbox reenables the distortion effect specified by the Four Corner coordinate parameters.
When the Four Corner checkbox is selected, value sliders to modify the X and Y coordinates of the layer’s four corner points (Bottom Left, Bottom Right, Top Right, and Top Left) become available. You can also control these parameters visually in the canvas using the Distort tool. See Transform tools in Motion.
Crop parameters
An activation checkbox that turns cropping on and off. If a layer is cropped and this checkbox is deselected, the layer resumes its original size, although the cropping values are maintained. Reselecting the checkbox reenables the cropping effect specified by the crop parameters.
When the Crop checkbox is selected, value sliders to modify the layer’s four edges (Left, Right, Bottom, and Top) become available. You can also control these parameters visually in the canvas using the Crop tool. See Crop a layer in Motion.
Timing parameters
Value sliders to control all aspects of clip retiming. See Intro to retiming media in the Motion Timeline.
Lighting parameters
The Lighting parameter controls appear only when the parent group is set to 3D.
Shading: A pop-up menu that sets how a layer responds to lights in the scene. There are three options:
Inherited: The layer uses the shading value of its parent.
On: The layer can be lit.
Off: The layer ignores lights.
Highlights: A checkbox that, when selected, causes lit layers to show highlights. This parameter has no effect if Shading is set to Off. Click the disclosure triangle to reveal an additional Shininess parameter.
Shininess: A slider that sets the strength of a layer’s highlights. Higher values create a glossier appearance. This parameter is disabled when the Highlights checkbox is deselected.
See Add lights in Motion.
Shadows parameters
The Shadows parameter controls appear only when the parent group is set to 3D.
Cast Shadows: A checkbox that sets whether a shadow is cast when a layer lies between a light source and another layer.
Note: This parameter does not affect drop shadows.
Receive Shadows: A checkbox that controls whether neighboring layers’ shadows affect the current layer. When this checkbox is deselected, light affects the layer as if the shadow-casting layer did not exist.
Shadows Only: A checkbox that, when selected, specifies that a layer blocks light and casts a shadow, while the layer itself does not appear in the scene.
Reflection parameters
The Reflection parameter controls appear only when the parent group is set to 3D. The Reflection parameter controls are not available for 3D particle emitters, 3D replicators, or normal text layers. However, the Reflection parameters are available for flattened text, which is activated by the Flatten checkbox in the Layout pane of the Text Inspector.
Reflectivity: A slider that controls the shininess of the layer’s surface. When set to 0%, there’s no reflectivity. When set to 100%, the layer is totally reflective, like a mirror.
Blur Amount: A slider that controls how blurry the reflection appears, creating the appearance of soft focus due to the surface quality of the reflecting layer.
Falloff: A checkbox that controls whether the reflection fades with distance from the layer, producing a more realistic result. Click the disclosure triangle to show additional controls that adjust the falloff effect: Begin Distance, End Distance, and Exponent. The Exponent slider adjusts how quickly the reflection becomes fainter as reflected layers move away from the reflecting layer.
Blend Mode: A pop-up menu that determines the blend mode used for the reflection.
Media parameters
The Media parameters (available when an image layer is selected) contain a thumbnail of the current layer and the “To” pop-up menu.
To: A pop-up menu that lets you choose another image layer in your project to replace the current layer. The replaced media remains in your project in the Media list.
Timing parameters
Use the Timing controls to set the selected object’s In and Out points, as well as the duration of the object. See Timing controls in Motion.
Download this guide: Apple Books | PDF