Account-driven enrolment methods with Apple devices
Account-driven User Enrolment and account-driven Device Enrolment provide a seamless, secure way for users and organisations to set up Apple devices for work by signing in with a Managed Apple Account.
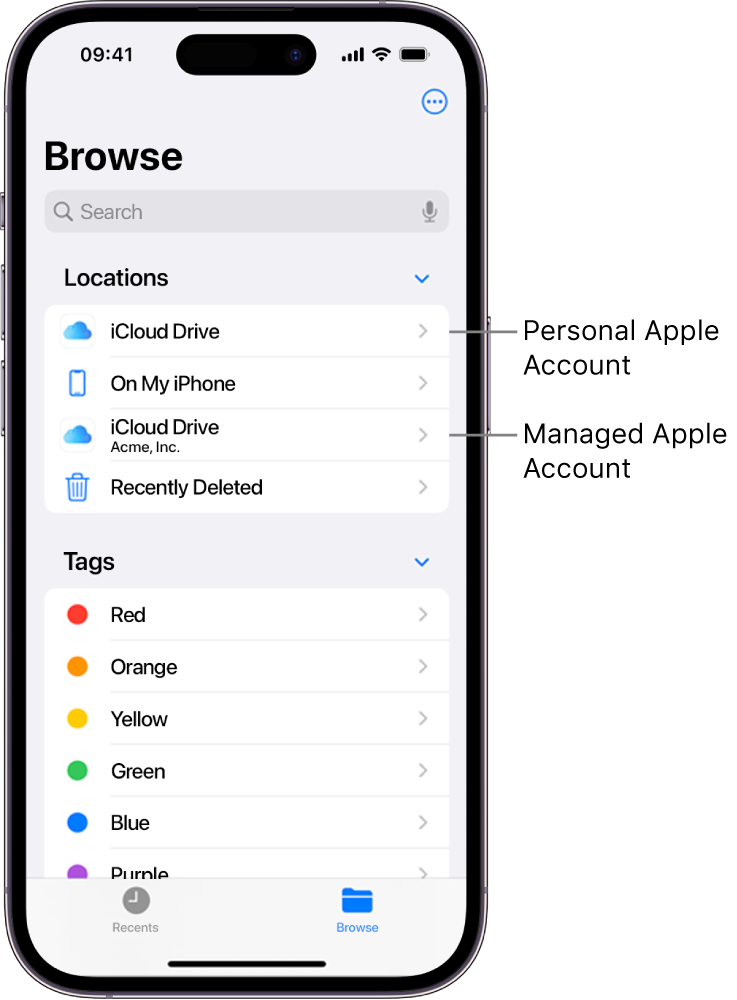
This approach allows both a Managed Apple Account and a personal Apple Account to be signed in on the same device, with complete separation of work and personal data. Users maintain privacy over their personal information, and IT supports work-related apps, settings and accounts.
To support this separation, the following changes have been made to the way apps and backups are handled:
All configurations and settings are removed when the enrolment profile is removed.
Managed apps are always removed during unenrolment.
If you install apps before enrolling in a device management service, you can’t convert them to become managed apps.
Restoring from a backup doesn’t restore device management service enrolment.
Users who sign in with their personal Apple Account can’t accept an invitation for managed app distribution.
Although you can create Managed Apple Accounts manually, organisations can take advantage of integrating with Google Workspace, Microsoft Entra ID or their identity provider (IdP).
For more information on federated authentication, see Intro to federated authentication with Apple School Manager or Intro to federated authentication with Apple Business Manager.
Account-driven enrolment process
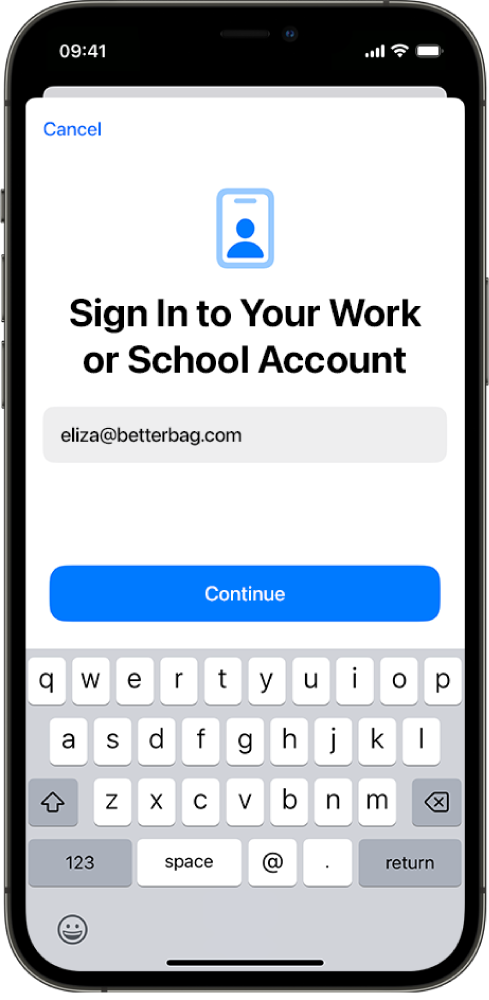
To enrol a device using account-driven User Enrolment or account-driven Device Enrolment, the user navigates to Settings > General > VPN & Device Management, or System Settings > General > Device Management, and selects the Sign In to Work or School Account button.
This initiates a four-stage process to enrol in a device management service:
Service discovery: The device determines the enrolment URL of the device management service.
Authentication and access token: The user provides credentials to authorise the enrolment and get an access token issued for ongoing authentication.
Service enrolment: The enrolment profile is sent to the device and the user is required to sign in with their Managed Apple Account to complete the enrolment.
Ongoing authentication: The device management service verifies the signed-in user on an ongoing basis using the access token.
Stage 1: Service discovery
In the first step, service discovery tries to identify the device management service’s enrolment URL. To do so, it uses the identifier the user enters, for example eliza@betterbag.com. The domain needs to be a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) that advertises the device management service for the user’s organisation.
The following then takes place:
Step 1
The device identifies the domain in the supplied identifier (in the above example, betterbag.com).
Step 2
The device requests the well-known resource from the organisation’s domain — for example, https://<domain>/.well-known/com.apple.remotemanagement.
The client includes two query parameters in the URL path of the HTTP GET request:
user-identifier: The value of the entered account identifier (in the above example, eliza@betterbag.com).
model-family: The device’s model family (for example, iPhone, iPad, Mac).
Note: The device follows HTTP 3xx redirect requests, which allows the actual com.apple.remotemanagement file to be hosted on another server reachable by the device.
For devices with iOS 18.2, iPadOS 18.2, macOS 15.2 or visionOS 2.2, or later, the service discovery process allows a device to fetch the well-known resource from an alternative location that the device management service specifies when linked to Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager. The first preference for service discovery is still the well-known resource at the organisation’s domain. If the request fails, the device proceeds to check with Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager for an alternative location of the well-known resource. This process requires that Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager verifies the domain within the identifier. For more information, see Add and verify a domain in Apple School Manager or Add and verify a domain in Apple Business Manager.
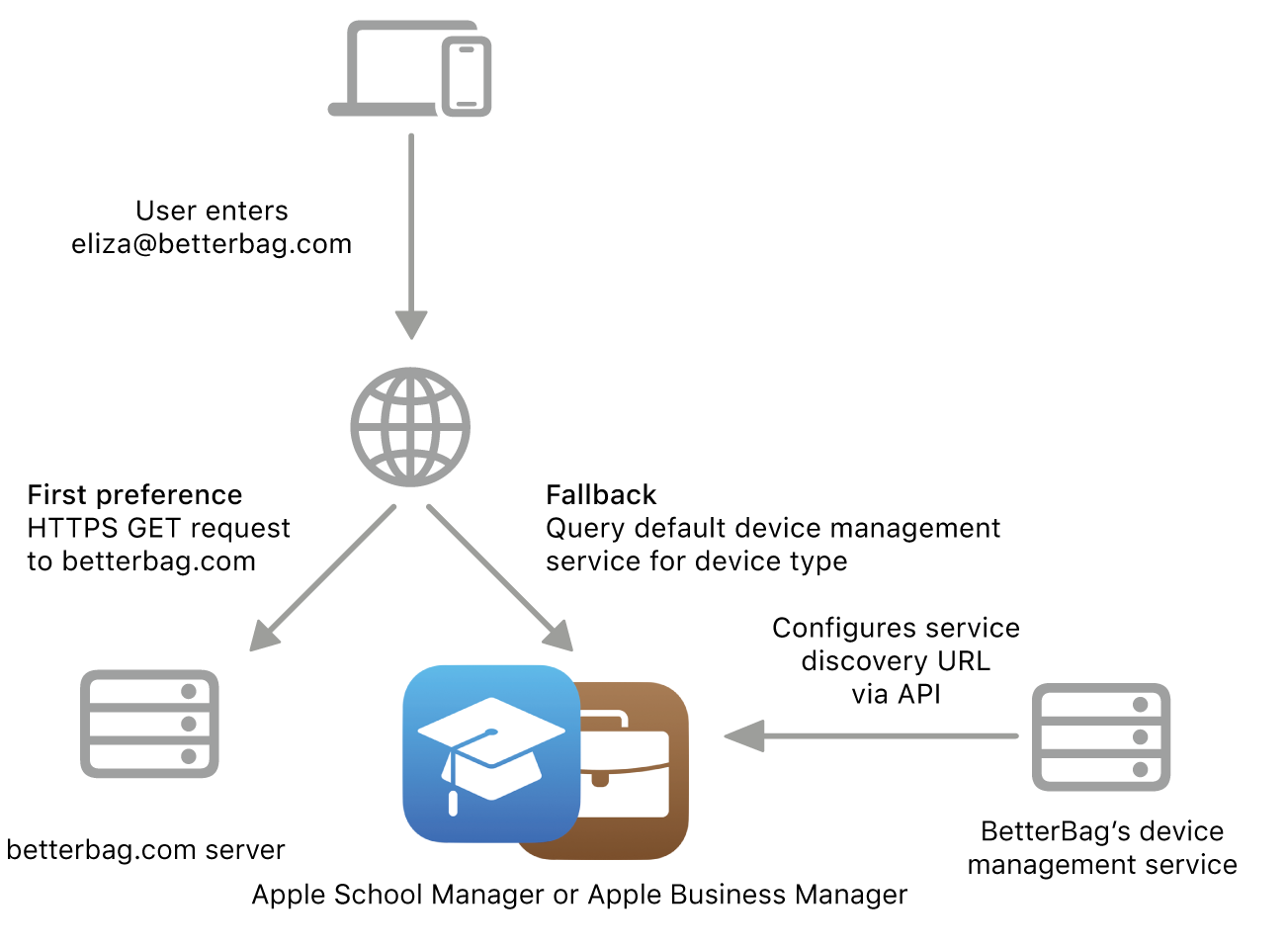
To use this capability, the device management service needs to configure the alternative service discovery URL when linked to Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager. When the device reaches out to Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager, the device type determines the assigned service for that type — the same process to determine the default service for Automated Device Enrolment. If the assigned service has a configured service discovery URL, the device proceeds to request the well-known resource from that location. To set the default device assignment, see Set the default device assignment in Apple School Manager or Set the default device assignment in Apple Business Manager.
The device management service can also host the well-known resource.
Step 3
The server hosting the well-known resource responds with a service discovery JSON document that conforms to the following schema:
{ "Servers": [ { "Version": "<Version>", "BaseURL": "<BaseURL>" } ]}The device management service enrolment keys, types and descriptions are in the following table. All keys are required.
Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Servers | Array | A list with a single entry. |
Version | String | This key determines the enrolment method to use and needs to be either |
BaseURL | String | The enrolment URL of the device management service. |
Important: The server needs to ensure that the Content-Type header field in the HTTP response is set to application/json.
Step 4
The device sends an HTTP POST request to the enrolment URL specified by the BaseURL.
Stage 2: Authentication and access token
To authorise the enrolment, the user needs to authenticate with the device management service. After successful authentication, the device management service issues an access token to the device. The device securely stores the token for use when authorising subsequent requests.
The access token:
Is central to both the initial authentication process and ongoing access to device management service resources
Serves as a secure bridge between the user’s Managed Apple Account and the device management service
Is used to allow continuous access to work resources for all account-driven enrolments
On iPhone, iPad and Apple Vision Pro, the initial and ongoing authentication process can be streamlined by using Enrolment SSO (Enrolment Single Sign-on) to reduce repeated authentication prompts. For more information, see Enrolment Single Sign-on for iPhone, iPad and Apple Vision Pro.
Stage 3: Device management service enrolment
Using the access token, the device can authenticate with the device management service and access the enrolment profile. This profile contains all information needed by the device to perform the enrolment. To complete the enrolment, the user needs to successfully sign in with their Managed Apple Account. After the enrolment is complete, the Managed Apple Account displays prominently within Settings and System Settings.
For more information on what iCloud services are available to users, see Access iCloud services.
Stage 4: Ongoing authentication
After the enrolment, the access token remains active and is included in all requests to the device management service using the Authorisation HTTP header. This allows the service to continuously verify the user and helps ensure that only authorised users retain access to organisational resources.
Access tokens typically expire after a set period. When this happens, the device may prompt the user to reauthenticate to renew the access token. Periodic revalidation helps to upload security, which is important for both personal and organisation-owned devices. With Enrolment SSO, token renewal happens automatically through the organisation’s identity provider, ensuring uninterrupted access without authenticating again.
How user data is separated from organisation data with account-driven enrolment methods
When account-driven User Enrolment or account-driven Device Enrolment is complete, the operating system automatically creates separate encryption keys on the device. If the user unenrols the device, or if the device management service remotely unenrols it, the operating system destroys those encryption keys. The operating system uses the keys to cryptographically separate the managed data listed in this table.
Content | Minimum supported operating system versions | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Managed app data containers | iOS 15 iPadOS 15 macOS 14 visionOS 1.1 | Managed apps use the Managed Apple Account associated with the device management service enrolment for iCloud data synchronisation. This includes managed apps (installed with the | |||||||||
Calendar app | iOS 16 iPadOS 16.1 macOS 13 visionOS 1.1 | Events are separate. | |||||||||
Keychain items | iOS 15 iPadOS 15 macOS 14 visionOS 1.1 | The third-party Mac app needs to use the Data Protection Keychain API. For more information, see the Global Variable kSecUseDataProtectionKeychain on the Apple Developer website. | |||||||||
Mail app | iOS 15 iPadOS 15 macOS 14 visionOS 1.1 | Mail attachments and body of the mail message are separate. | |||||||||
Notes app | iOS 15 iPadOS 15 macOS 14 visionOS 1.1 | Notes are separate. | |||||||||
Reminders app | iOS 17 iPadOS 17 macOS 14 visionOS 1.1 | Reminders are separate. | |||||||||
On iPhone, iPad and Apple Vision Pro, managed apps and managed web-based documents all have access to an organisation’s iCloud Drive (which appears separately in the Files app after a user signs in with their Managed Apple Account). The device management service administrator can help keep specific personal and organisational documents separate by using specific restrictions. For more information, see Distribute managed apps to Apple devices.
If a user is signed in with a personal Apple Account and Managed Apple Account, Sign in with Apple automatically uses the Managed Apple Account for managed apps and the personal Apple Account for unmanaged apps. When using a sign-in flow in Safari or SafariWebView within a managed app, the user can select and enter their Managed Apple Account to associate the sign-in with their work or school account.