Final Cut Pro X User Guide
- Welcome
-
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.4.9
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.4.7
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.4.6
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.4.4
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.4.1
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.4
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.3
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.2
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.1.2
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.1
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.0.6
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.0.3
- What’s new in Final Cut Pro 10.0.1
-
- Intro to effects
-
- Intro to transitions
- How transitions are created
- Add transitions
- Set the default transition
- Delete transitions
- Adjust transitions in the timeline
- Adjust transitions in the inspector and viewer
- Merge jump cuts with the Flow transition
- Adjust transitions with multiple images
- Modify transitions in Motion
-
- Add storylines
- Use the precision editor
- Conform frame sizes and rates
- Use XML to transfer projects
-
-
- Intro to media management
-
- View a clip’s information
- Override a clip’s metadata
- Locate source media files
- Relink clips to media files
- Consolidate projects and libraries
- Back up projects and libraries
- Create optimized and proxy files
- Create a proxy-only project
- Manage render files
- View background tasks
- Convert incompatible media
- Create camera archives
- Glossary
- Copyright

Intro to audio editing in Final Cut Pro
Final Cut Pro includes tools for editing audio clips or multiple audio channels. You edit audio in two ways, detailed below.
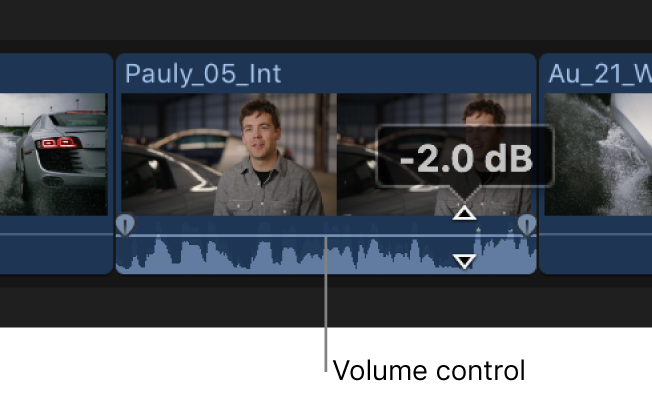
Clip-level audio editing
You can make audio adjustments and edits to whole clips. At this level, audio adjustments and effects are applied to the entire clip, including any audio channels within the clip. Final Cut Pro preserves any adjustments you make to individual audio channels. This means that if you reduce the volume for a single channel but raise the volume for the whole clip, the volume of the single channel is raised but stays in proportion to the volume of other channels in the clip.
If your source media contains only one or two audio channels or you’re editing an audio-only clip, you may only need to make adjustments and edits at this level.
Advanced multichannel audio editing
Final Cut Pro automatically groups channels into audio components according to how the channels are configured for the clip. You can expand the audio portion of clips to reveal and edit audio components down to the individual channel level. This allows you to apply different effects to different components and streamlines the process for making quick sound cutouts to a single microphone input or other fine adjustments.
Important: Many digital audio file formats, such as AAC and MP3, use interleaved stereo files, which do not contain separate left and right channels. These files appear as a single audio component unless you change the clip’s channel configuration.
Keep in mind the following when editing audio components in Final Cut Pro:
You view and change the audio channel configuration of your clips in the Audio Configuration section of the Audio inspector. You can enable or disable audio components and configure channels in mono, stereo, and surround formats. See Configure audio channels in Final Cut Pro.
With the Range Selection tool, you can quickly select ranges within an audio component to target the audio you want to edit.
When you show audio components for compound clips, multicam clips, and synced clips, Final Cut Pro presents role components, which you can edit in the same way you edit standard components. See Work with audio roles in compound clips in Final Cut Pro.
You edit audio components in the same way you edit whole clips. You can:
Skim individual components when clip skimming and audio skimming are turned on. See Skim media in Final Cut Pro.
Adjust the volume of a component. See Adjust volume in Final Cut Pro.
Mute a component’s audio by disabling or silencing all or a portion of the component. This is the fastest way to remove unwanted sounds from a component. See Solo and mute audio clips in Final Cut Pro.
Trim a component’s start and end points. See Extend or shorten clips in Final Cut Pro.
Perform a roll edit on adjacent audio components. See Make roll edits in Final Cut Pro.
Apply fades or use fade handles to fade audio in at the beginning of an audio component, or fade audio out at the end. See Fade audio in and out in Final Cut Pro.
Pan the sound for individual components. See Pan audio in Final Cut Pro.
Assign a role (specifically, a subrole) to a component. See Intro to roles in Final Cut Pro and View and reassign roles in Final Cut Pro.
Add or adjust audio effects for individual components. See Add audio effects in Final Cut Pro or Adjust audio effects in Final Cut Pro.
Adjust audio effects for individual components using keyframes. See Keyframe audio effects in Final Cut Pro.
For examples of multichannel audio editing workflows, see Final Cut Pro multichannel audio editing examples.