Logic Pro User Guide
- Welcome
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Workflow overview
- Logic Pro project basics
- Advanced tools and additional options
- Undo and redo edits
- Manage Logic Pro content
- How to get help
-
- Projects overview
- Create projects
- Open projects
- Save projects
- Delete projects
-
- Play a project
- Set the playhead position
- Control playback with the transport buttons
- Use transport shortcut menus
- Use transport keyboard shortcuts
- Customize the control bar
- Change the LCD display mode
- Monitor and reset MIDI events
- Use the cycle area
- Use the Chase Events function
- Control Logic Pro using Apple Remote
- Control Logic Pro projects using Logic Remote
- Preview projects in the Finder
- Close projects
- View project information
-
- Overview
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Play software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Overdub software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Use Note Repeat
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Use step input recording techniques
- Use the metronome
-
- Overview
-
- Regions overview
- Select regions
- Select parts of regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Add or remove gaps
- Delay region playback
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Resize regions
- Mute and solo regions
- Time stretch regions
- Split regions
- Demix MIDI regions
- Join regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Normalize audio regions in the Tracks area
- Create aliases of MIDI regions
- Clone audio regions
- Convert repeated MIDI regions to loops
- Change the color of regions
- Convert audio regions to Sampler zones
- Rename regions
- Delete regions
-
- Overview
-
- Add notes
- Select notes
- Snap items to the grid
- Move notes
- Copy notes
- Change the pitch of notes
- Resize notes
- Edit note velocity
- Quantize the timing of notes
- Quantize the pitch of notes
- Change note articulations
- Lock the position of events
- Mute notes
- Change note color
- View note labels
- Delete notes
- Time stretch notes
- View multiple MIDI regions
- Split chords
- Automation/MIDI area in the Piano Roll Editor
- Open other editors
-
- Flex Time and Pitch overview
-
- Flex Pitch algorithm and parameters
- Edit the pitch of audio in the Audio Track Editor or a zoomed in track
- Edit the pitch of audio in the Tracks area when the track is not zoomed in
- Correct the timing of audio regions with Flex Pitch
- Quantize the pitch of audio regions
- Create MIDI from audio recordings
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Use Varispeed to alter the speed and pitch of audio
-
- Mixing overview
- Set channel strip input formats
- Set channel strip pan or balance positions
- Mute and solo channel strips
-
- Plug-ins overview
- Add, remove, move, and copy plug-ins
- Insert a plug-in on a track using drag and drop
- Activate plug-ins on inactive channels
- Use the Channel EQ
- Work in the plug-in window
- Work with plug-in settings
- Work with plug-in latencies
- Work with Audio Units plug-ins
- Support for ARA 2 compatible plug-ins
- Use the Plug-in Manager
- Work with channel strip settings
- Surround panning
- Use the I/O Labels window
- Undo and redo Mixer and plug-in adjustments
-
- Smart Controls overview
- Show Smart Controls for master effects
- Choose a Smart Control layout
- Automatic MIDI controller assignment
- Map screen controls automatically
- Map screen controls
- Edit mapping parameters
- Use parameter mapping graphs
- Open the plug-in window for a screen control
- Rename a screen control
- Use articulation IDs to change articulations
- Assign hardware controls to screen controls
- Compare Smart Control edits with saved settings in Logic Pro
- Use the Arpeggiator
- Automate screen control movements
-
- Live Loops overview
- Start and stop cells
- Work with Live Loops cells
- Change loop settings for cells
- How the Live Loops grid and Tracks area interact
- Edit cells
- Edit scenes
- Work in the Cell Editor
- Bounce cells
- Record a Live Loops performance
- Change Live Loops grid settings
- Control Live Loops in Logic Pro with other devices
-
- Overview
- Add notes
-
- Part box overview
- View score symbols
- Select score symbols
- Add notes and rests
- Add notes and symbols to multiple regions
- Add key and time signature changes
- Change the clef sign
- Add dynamic marks, slurs, and crescendi
- Change note heads
- Add symbols to notes
- Add trills, ornaments, and tremolo symbols
- Add sustain pedal markings
- Add chord symbols
- Add chord grids and tablature symbols
- Add bar lines, repeats, and coda signs
- Add page and line break symbols
-
- Select notes
- Move and copy notes
- Change note pitch, duration, and velocity
- Change note articulations
- Quantize the timing of notes
- Restrict note input to the current key
- Control how ties are displayed
- Add and edit tuplets
- Override display quantization using tuplets
- Add grace notes and independent notes
- Delete notes
- Use automation in the Score Editor
-
- Staff styles overview
- Assign staff styles to tracks
- Staff Style window
- Create and duplicate staff styles
- Edit staff styles
- Edit staff, voice, and assign parameters
- Add and delete staffs or voices in the Logic Pro Staff Style window
- Copy staffs or voices in the Logic Pro Staff Style window
- Copy staff styles between projects
- Delete staff styles
- Assign notes to voices and staffs
- Display polyphonic parts on separate staffs
- Change the staff assignment of score symbols
- Beam notes across staffs
- Use mapped staff styles for drum notation
- Predefined staff styles
- Share a score
-
- Environment overview
- Common object parameters
- Customize the Environment
-
-
- Fader objects overview
- Use fader objects
- Play back fader movements
- Work with object groups
- Fader styles
- Fader functions: MIDI events
- Fader functions: range, value as
- Fader functions: filter
- Vector fader
- Special faders overview
- Cable switchers
- Meta event faders
- SysEx faders
- Work with SysEx messages
- Special functions
- Ornament objects
- MMC record buttons
- Keyboard objects
- Monitor objects
- Channel splitter object
- Physical input objects
- Physical input objects
- MIDI click objects
-
-
- Key commands overview
- Browse, import, and save key commands
- Assign key commands
- Copy and print key commands
-
- Global Commands key commands
- Global Control Surfaces Commands
- Various windows
- Windows Showing Audio files
- Main Window Tracks and Various Editors
- Live Loops Grid
- Various Editors
- Views showing Time Ruler
- Main Window Tracks
- Mixer
- MIDI Environment
- Piano Roll
- Score Editor
- Event Editor
- Step Editor
- Step Sequencer
- Project Audio
- Audio File Editor
- Smart Tempo Editor
- Sampler
- Step Input Keyboard
- Tool key commands in Logic Pro
- Touch Bar shortcuts
-
-
- Working with your control surface
- Connect control surfaces
- Add a control surface to Logic Pro
- Automatic assignment for USB MIDI controllers
- Grouping control surfaces
- Control Surfaces preferences overview
- Modal dialog display
- Tips for using your control surface
- Control surfaces supported by Logic Pro
- Software and firmware
-
-
- Learn about Effects
-
- Learn about Amps and Pedals
-
- Bass Amp Designer overview
- Bass amplifier models
- Bass cabinet models
- Build a custom combo
- Amplifier signal flow
- Pre-amp signal flow
- Use the D.I. box
- Amplifier controls
- Bass Amp Designer effects overview
- Bass Amp Designer EQ
- Bass Amp Designer compressor
- Bass Amp Designer Graphic EQ
- Bass Amp Designer Parametric EQ
- Bass Amp Designer microphone controls
-
- Use MIDI plug-ins
-
- Arpeggiator overview
- Arpeggiator control parameters
- Note order parameters overview
- Note order variations
- Note order inversions
- Arpeggiator pattern parameters overview
- Use Live mode
- Use Grid mode
- Arpeggiator options parameters
- Arpeggiator keyboard parameters
- Use keyboard parameters
- Assign controller parameters
- Modifier MIDI plug-in controls
- Note Repeater MIDI plug-in controls
- Randomizer MIDI plug-in controls
-
- Use the Scripter MIDI plug-in
- Use the Script Editor
- Scripter API overview
- MIDI processing functions overview
- HandleMIDI function
- ProcessMIDI function
- GetParameter function
- SetParameter function
- ParameterChanged function
- Reset function
- JavaScript objects overview
- Use the JavaScript Event object
- Use the JavaScript TimingInfo object
- Use the Trace object
- Use the MIDI event beatPos property
- Use the JavaScript MIDI object
- Create Scripter controls
- Transposer MIDI plug-in controls
-
- Learn about included Instruments
-
- Alchemy overview
- Name bar
-
- Alchemy source overview
- Source master controls
- Import browser
- Source subpage controls
- Source filter controls
- Source filter use tips
- Source elements overview
- Additive element controls
- Additive element effects
- Spectral element controls
- Spectral element effects
- Pitch correction controls
- Formant filter controls
- Granular element controls
- Sampler element controls
- VA element controls
- Source modulations
- Morph controls
- Master voice section
- Alchemy extended parameters
-
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler overview
- Add content to Logic Pro Quick Sampler
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler waveform display
- Use Flex in Logic Pro Quick Sampler
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler Pitch controls
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler Filter controls
- Quick Sampler filter types
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler Amp controls
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler extended parameters
-
- Sculpture overview
- Sculpture interface
- Global parameters
- Amplitude envelope parameters
- Use the Waveshaper
- Filter parameters
- Output parameters
- Use surround range and diversity
- Assign MIDI controllers
- Extended parameters
-
-
- Ultrabeat overview
- Ultrabeat interface
- Synthesizer section overview
- Filter section controls
- Distortion circuit controls
- Glossary

Global Score settings in Logic Pro
Global Score settings define global formatting options, such as page margins, note spacing, bars per line, and more.
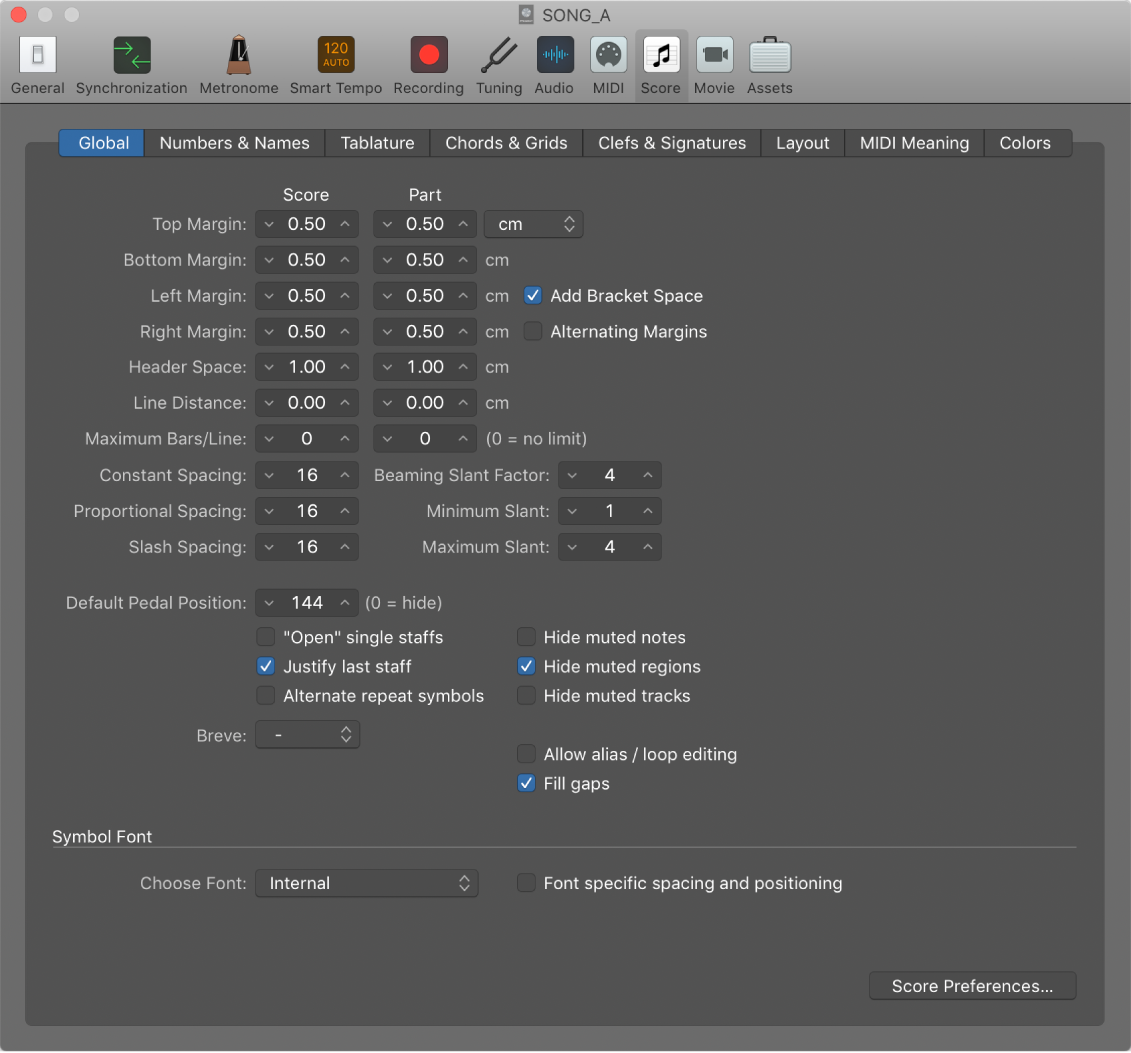
![]() When Show Advanced Tools is selected in Advanced preferences, the following are available:
When Show Advanced Tools is selected in Advanced preferences, the following are available:
Top, Bottom, Left, and Right Margin fields: These values show the margin distances (in cm or inch) to the outer border of the printable area on the page. A “Top Margin 0.0 inches” value means that printing starts as close to the top of the paper as the selected printer driver allows. This also means that the size of the printable area can vary between printers, although the difference should be minimal.
Add Bracket Space checkbox: Creates additional space between the left margin line and the beginning of staffs, for braces and brackets. If unselected, staffs are aligned directly along the left margin line.
Alternating Margins checkbox: If selected, the left and right page margin settings are swapped on every second page. This can be useful if a score is going to be bound as a book: the inner margin usually needs to be a little bigger than the outer one. It’s also possible that the opposite might be preferable, in cases where extra space is needed for remarks that may be added to the score at a later date.
Header Space field: Defines the height reserved for headers, between the top margin of the first page and the top margin of the first staff on the page (as per the assigned staff style).
Note: Text objects inserted directly into this area automatically become global text elements, and are displayed as headers in all score sets (full scores and parts).
You can also be change this value directly in the score, by dragging the purple line above the first staff.
Line Distance field: Defines additional vertical distance between staff systems (single, multiple, or bracketed staffs can constitute a system) on the same page. It applies to full scores, as well as single staff parts.
Maximum Bars/Line field: This parameter can be useful when using small spacing values (see below), to prevent too many bars from being displayed on one line. The number set here limits the number of bars that can be displayed per line.
Note: This setting can be overridden when using the Layout tool to change line breaks.
Constant Spacing field: Determines the amount of horizontal distance between notes, affecting the distance from note to note, regardless of rhythmic value.
Proportional Spacing field: Determines the amount of horizontal distance between notes, taking the note durations into consideration.
If you only use Proportional Spacing (and set Constant Spacing to 0), every bar receives the same amount of horizontal space. A whole note uses as much space as four quarter notes. In the opposite situation (high constant value, proportional value set to 0), the distance from one note to the next is always the same, regardless of note duration. A half note takes the same amount of space as an eighth note. Other factors, such as accidentals, ties, and so on, are also considered for note distance calculations.
Slash Spacing field: This is the distance parameter for slashes (used in staff styles that display beat slashes instead of automatic rests), and is important when inserting notes into staffs that display slashes. For example, musical styles such as funk use a lot of sixteenth notes, so you are likely to choose a higher slash distance than you would for music that doesn’t go beyond eighth notes. This way, the proper relationships between notes and passages (containing only slashes and chord symbols) can be maintained.
Beaming Slant Factor, Minimum Slant, and Maximum Slant fields: These three parameters affect the slant angle of beams. As with the Spacing parameters, these parameters work together. Appropriate settings need to be found by trying different combinations. The final settings vary, depending on the style of the music and on personal preference.
Beaming Slant Factor field: Determines the general amount of beam slanting, in relation to the intervals of the notes connected by beams.
Minimum Slant field: Determines the minimum interval of notes that causes beams to be slanted.
Maximum Slant field: Determines the maximum beaming slant angle.
These parameters work relative to a particular scoring situation, which is why no explicit settings can be given. Again, it’s essential to try different combinations when working on the final layout of a piece.
Default Pedal Position field: Determines the vertical position of automatic pedal symbols (those created when you use the MIDI sustain pedal during a real-time recording). If set to zero, recorded MIDI sustain pedal events are hidden in the score. Pedal marks that you manually insert from the Part box are not affected by this parameter.
“’Open’ single staffs” checkbox: Displays single staffs without vertical lines at their start point (left side of the clef).
“Justify last staff” checkbox: Lengthens the last line (the last staff system, in full scores) to the right page margin.
“Alternate repeat symbols” checkbox: If selected, all repeat signs in the project are displayed with real book-style brackets.
“Hide muted notes” checkbox: Excludes muted notes from the score display. If unselected, muted notes are displayed in the score, even though they won’t be heard during MIDI playback.
“Hide muted regions” checkbox: Excludes muted regions from the score display. If unselected, muted regions are displayed in the score, even though they won’t be heard during MIDI playback.
“Hide muted tracks” checkbox: Excludes muted tracks from the score display. If unselected, muted tracks are displayed in the score, even though they won’t be heard during MIDI playback.
Choose Font pop-up menu: Choose from any installed scoring (symbol) fonts, such as the Sonata font.
“Font specific spacing and positioning” checkbox: If selected, the Score Editor displays symbols with spacing and positioning specific to the chosen symbol font.
Score Preferences button: Opens the Score preferences window.
![]() When Additional Score Options is selected in Advanced preferences, the following are available:
When Additional Score Options is selected in Advanced preferences, the following are available:
“Allow alias/loop editing” checkbox: Switches alias/loop editing on or off.
“Fill gaps” checkbox: Fills gaps between regions to display a continuous staff.
Breve pop-up menu: Choose from four different shapes of breve notes, as well as the default no breve setting (which disables any breve notes).