Logic Pro User Guide
- Welcome
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Workflow overview
- Logic Pro project basics
- Advanced tools and additional options
- Undo and redo edits
- Manage Logic Pro content
- How to get help
-
- Projects overview
- Create projects
- Open projects
- Save projects
- Delete projects
-
- Play a project
- Set the playhead position
- Control playback with the transport buttons
- Use transport shortcut menus
- Use transport keyboard shortcuts
- Customize the control bar
- Change the LCD display mode
- Monitor and reset MIDI events
- Use the cycle area
- Use the Chase Events function
- Control Logic Pro using Apple Remote
- Control Logic Pro projects using Logic Remote
- Preview projects in the Finder
- Close projects
- View project information
-
- Overview
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Play software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Overdub software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Use Note Repeat
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Use step input recording techniques
- Use the metronome
-
- Overview
-
- Regions overview
- Select regions
- Select parts of regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Add or remove gaps
- Delay region playback
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Resize regions
- Mute and solo regions
- Time stretch regions
- Split regions
- Demix MIDI regions
- Join regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Normalize audio regions in the Tracks area
- Create aliases of MIDI regions
- Clone audio regions
- Convert repeated MIDI regions to loops
- Change the color of regions
- Convert audio regions to Sampler zones
- Rename regions
- Delete regions
-
- Overview
-
- Add notes
- Select notes
- Snap items to the grid
- Move notes
- Copy notes
- Change the pitch of notes
- Resize notes
- Edit note velocity
- Quantize the timing of notes
- Quantize the pitch of notes
- Change note articulations
- Lock the position of events
- Mute notes
- Change note color
- View note labels
- Delete notes
- Time stretch notes
- View multiple MIDI regions
- Split chords
- Automation/MIDI area in the Piano Roll Editor
- Open other editors
-
- Flex Time and Pitch overview
-
- Flex Pitch algorithm and parameters
- Edit the pitch of audio in the Audio Track Editor or a zoomed in track
- Edit the pitch of audio in the Tracks area when the track is not zoomed in
- Correct the timing of audio regions with Flex Pitch
- Quantize the pitch of audio regions
- Create MIDI from audio recordings
- Change the gain of notes in audio regions
- Use Varispeed to alter the speed and pitch of audio
-
- Mixing overview
- Set channel strip input formats
- Set channel strip pan or balance positions
- Mute and solo channel strips
-
- Plug-ins overview
- Add, remove, move, and copy plug-ins
- Insert a plug-in on a track using drag and drop
- Activate plug-ins on inactive channels
- Use the Channel EQ
- Work in the plug-in window
- Work with plug-in settings
- Work with plug-in latencies
- Work with Audio Units plug-ins
- Support for ARA 2 compatible plug-ins
- Use the Plug-in Manager
- Work with channel strip settings
- Surround panning
- Use the I/O Labels window
- Undo and redo Mixer and plug-in adjustments
-
- Smart Controls overview
- Show Smart Controls for master effects
- Choose a Smart Control layout
- Automatic MIDI controller assignment
- Map screen controls automatically
- Map screen controls
- Edit mapping parameters
- Use parameter mapping graphs
- Open the plug-in window for a screen control
- Rename a screen control
- Use articulation IDs to change articulations
- Assign hardware controls to screen controls
- Compare Smart Control edits with saved settings in Logic Pro
- Use the Arpeggiator
- Automate screen control movements
-
- Live Loops overview
- Start and stop cells
- Work with Live Loops cells
- Change loop settings for cells
- How the Live Loops grid and Tracks area interact
- Edit cells
- Edit scenes
- Work in the Cell Editor
- Bounce cells
- Record a Live Loops performance
- Change Live Loops grid settings
- Control Live Loops in Logic Pro with other devices
-
- Overview
- Add notes
-
- Part box overview
- View score symbols
- Select score symbols
- Add notes and rests
- Add notes and symbols to multiple regions
- Add key and time signature changes
- Change the clef sign
- Add dynamic marks, slurs, and crescendi
- Change note heads
- Add symbols to notes
- Add trills, ornaments, and tremolo symbols
- Add sustain pedal markings
- Add chord symbols
- Add chord grids and tablature symbols
- Add bar lines, repeats, and coda signs
- Add page and line break symbols
-
- Select notes
- Move and copy notes
- Change note pitch, duration, and velocity
- Change note articulations
- Quantize the timing of notes
- Restrict note input to the current key
- Control how ties are displayed
- Add and edit tuplets
- Override display quantization using tuplets
- Add grace notes and independent notes
- Delete notes
- Use automation in the Score Editor
-
- Staff styles overview
- Assign staff styles to tracks
- Staff Style window
- Create and duplicate staff styles
- Edit staff styles
- Edit staff, voice, and assign parameters
- Add and delete staffs or voices in the Logic Pro Staff Style window
- Copy staffs or voices in the Logic Pro Staff Style window
- Copy staff styles between projects
- Delete staff styles
- Assign notes to voices and staffs
- Display polyphonic parts on separate staffs
- Change the staff assignment of score symbols
- Beam notes across staffs
- Use mapped staff styles for drum notation
- Predefined staff styles
- Share a score
-
- Environment overview
- Common object parameters
- Customize the Environment
-
-
- Fader objects overview
- Use fader objects
- Play back fader movements
- Work with object groups
- Fader styles
- Fader functions: MIDI events
- Fader functions: range, value as
- Fader functions: filter
- Vector fader
- Special faders overview
- Cable switchers
- Meta event faders
- SysEx faders
- Work with SysEx messages
- Special functions
- Ornament objects
- MMC record buttons
- Keyboard objects
- Monitor objects
- Channel splitter object
- Physical input objects
- Physical input objects
- MIDI click objects
-
-
- Key commands overview
- Browse, import, and save key commands
- Assign key commands
- Copy and print key commands
-
- Global Commands key commands
- Global Control Surfaces Commands
- Various windows
- Windows Showing Audio files
- Main Window Tracks and Various Editors
- Live Loops Grid
- Various Editors
- Views showing Time Ruler
- Main Window Tracks
- Mixer
- MIDI Environment
- Piano Roll
- Score Editor
- Event Editor
- Step Editor
- Step Sequencer
- Project Audio
- Audio File Editor
- Smart Tempo Editor
- Sampler
- Step Input Keyboard
- Tool key commands in Logic Pro
- Touch Bar shortcuts
-
-
- Working with your control surface
- Connect control surfaces
- Add a control surface to Logic Pro
- Automatic assignment for USB MIDI controllers
- Grouping control surfaces
- Control Surfaces preferences overview
- Modal dialog display
- Tips for using your control surface
- Control surfaces supported by Logic Pro
- Software and firmware
-
-
- Learn about Effects
-
- Learn about Amps and Pedals
-
- Bass Amp Designer overview
- Bass amplifier models
- Bass cabinet models
- Build a custom combo
- Amplifier signal flow
- Pre-amp signal flow
- Use the D.I. box
- Amplifier controls
- Bass Amp Designer effects overview
- Bass Amp Designer EQ
- Bass Amp Designer compressor
- Bass Amp Designer Graphic EQ
- Bass Amp Designer Parametric EQ
- Bass Amp Designer microphone controls
-
- Use MIDI plug-ins
-
- Arpeggiator overview
- Arpeggiator control parameters
- Note order parameters overview
- Note order variations
- Note order inversions
- Arpeggiator pattern parameters overview
- Use Live mode
- Use Grid mode
- Arpeggiator options parameters
- Arpeggiator keyboard parameters
- Use keyboard parameters
- Assign controller parameters
- Modifier MIDI plug-in controls
- Note Repeater MIDI plug-in controls
- Randomizer MIDI plug-in controls
-
- Use the Scripter MIDI plug-in
- Use the Script Editor
- Scripter API overview
- MIDI processing functions overview
- HandleMIDI function
- ProcessMIDI function
- GetParameter function
- SetParameter function
- ParameterChanged function
- Reset function
- JavaScript objects overview
- Use the JavaScript Event object
- Use the JavaScript TimingInfo object
- Use the Trace object
- Use the MIDI event beatPos property
- Use the JavaScript MIDI object
- Create Scripter controls
- Transposer MIDI plug-in controls
-
- Learn about included Instruments
-
- Alchemy overview
- Name bar
-
- Alchemy source overview
- Source master controls
- Import browser
- Source subpage controls
- Source filter controls
- Source filter use tips
- Source elements overview
- Additive element controls
- Additive element effects
- Spectral element controls
- Spectral element effects
- Pitch correction controls
- Formant filter controls
- Granular element controls
- Sampler element controls
- VA element controls
- Source modulations
- Morph controls
- Master voice section
- Alchemy extended parameters
-
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler overview
- Add content to Logic Pro Quick Sampler
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler waveform display
- Use Flex in Logic Pro Quick Sampler
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler Pitch controls
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler Filter controls
- Quick Sampler filter types
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler Amp controls
- Logic Pro Quick Sampler extended parameters
-
- Sculpture overview
- Sculpture interface
- Global parameters
- Amplitude envelope parameters
- Use the Waveshaper
- Filter parameters
- Output parameters
- Use surround range and diversity
- Assign MIDI controllers
- Extended parameters
-
-
- Ultrabeat overview
- Ultrabeat interface
- Synthesizer section overview
- Filter section controls
- Distortion circuit controls
- Glossary

Logic Pro Alchemy main filter controls
Main filter components are shown only in advanced view. Click the Advanced button to switch to advanced view, then click the Global button.
There are two main filter modules, labeled Filter 1 and Filter 2. The filters can operate in parallel or in series.
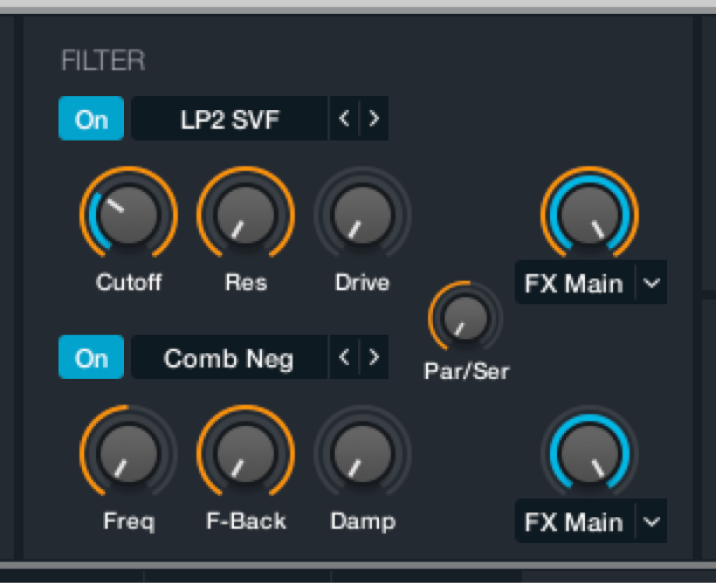
The output from all four sources is sent to the main filters at levels determined by independent controls in each source. Both main filter modules provide multi-mode filters with identical controls.
Note: It is possible for each source to completely bypass the main filters, or to send a portion of the source signal to the main filters and another portion directly to the effects section. Though you can use filters at multiple locations in the signal path, you can often attain the same or similar results by careful use of fewer filters, which helps to reduce CPU load.
Main filter parameters
On/Off buttons: Enable or disable each filter.
Filter type pop-up menus and fields: Choose the filter type. Use the descriptive names: Clean, Edgy, Gritty, Rich, Sharp, and Smooth to make a choice that is right for your sound. You can step through the available filter types with the Previous and Next buttons (the arrows). See Logic Pro Alchemy filter types.
Note: The chosen filter type can alter the names and functions of the default Cutoff, Resonance, and Drive knobs.
Cutoff knobs and fields: Set the cutoff frequency for the chosen filter type.
Resonance knobs and fields: Boost or cut frequencies above, below, or surrounding the value set with the Cutoff knob. Resonance behavior changes when different filter types are chosen.
Drive knobs and fields: Overdrive the filter. This can lead to intense distortions and aliasing, depending on filter type.
VU meters: Indicate the current audio level received from all four sources. If the filter input level exceeds 0dB, the VU meters indicate clipping by momentarily turning red. Clipping produces an undesirable digital audio artifact in the output stage. If clipping occurs, reduce the Vol knob of the loudest source or adjust the balance between sources.
Par/Ser knob and field: Set the filter routing configuration. Note that this is pre-effects.
At 0% position, the total output of Filter 1 is sent to the main outputs of the filter module. This is parallel mode.
At 100% position, the total output of Filter 1 is sent to the Filter 2 input. This is series mode.
At 50% position, equal amounts of the Filter 1 output signal are sent to the Filter 2 input and the main outputs of the filter module.
Note: When the Par/Ser knob is set to 100%, a portion of the Filter 1 signal bypasses Filter 2 whenever the Filter 1 FX Master knob is set above 0%.
FX master knobs: Determine the balance between the filter module output sent to the effects section and the filter module output sent directly to the Alchemy main output.
At 0% position, the total filter output is sent to the Alchemy main outputs, and none of it to the effects section.
At 100% position, the total filter output is sent to the effects section, and none of it to the Alchemy main outputs.
At 50% position, equal amounts of filter output signal are sent to the effects section and the Alchemy main outputs.
Send destination pop-up menus: Independently send the output of main filter 1 or 2 to the Main effects rack, or to the A/B/C/D effects rack. Choose FX Main, FX A, FX B, FX C, or FX D.
Note: When the FX master knob for filter 1 or 2 is at the full-left position, the total filter 1 or 2 output is sent to the Alchemy main outputs, and none of it to the effects section.
Create vowel sounds with parallel source filters
Vowel sounds in human speech are the result of formants produced by changing the shape of the vocal cavity. By mimicking these formants, Alchemy can produce speech- or song-like effects, even in VA mode without samples of actual speech.
In Logic Pro, from the Name bar, click the File button and choose Initialize Preset from the pop-up menu to reset all Alchemy parameters to default settings.
Click the source A button, then make the following parameter changes:
Set Vol to 0 dB.
Set Coarse Tune to –12 semis.
Click the source A Fine Tune knob.
In the top slot of the modulation rack, choose LFO > LFO 1 from the pop-up menu, then set the Mod Depth knob to a value near 50%.
In the LFO 1 control panel, set Attack to approximately 0.50 sec, turn off Sync, and set Rate to approximately 5 Hz.
Enable filter 1 by clicking the On button next to the filter type pop-up menu. Do the same for filters 2 and 3. Click the Par(allel) button to enable parallel configuration of the source A filters.
Click the Global button to view all sources, then click the source A content field and choose Copy Source from the pop-up menu.
Click the source B content field, and choose Paste Source from the pop-up menu. Repeat for the source C and D content fields.
Click the A button to view source A, then make the following (approximate) parameter changes to create an “ahhh” sound:
Cutoff 1 = 800 Hz, Res 1 = 87%
Cutoff 2 = 1200 Hz, Res 2 = 87%
Cutoff 3 = 2800 Hz, Res 3 = 87%
Click the B button to view source B, then make the following (approximate) parameter changes to create an “eeeh” sound:
Cutoff 1 = 230 Hz, Res 1 = 87%
Cutoff 2 = 2600 Hz, Res 2 = 75%
Cutoff 3 = 3200 Hz, Res 3 = 75%
Click the C button to view source C, then make the following (approximate) parameter changes to create an “oooh” sound:
Cutoff 1 = 200 Hz, Res 1 = 87%
Cutoff 2 = 880 Hz, Res 2 = 65%
Cutoff 3 = 2400 Hz, Res 3 = 50%
Click the D button to view source D, then make the following (approximate) parameter changes to create an “ehh” sound:
Cutoff 1 = 530 Hz, Res 1 = 65%
Cutoff 2 = 1850 Hz, Res 2 = 75%
Cutoff 3 = 2500 Hz, Res 3 = 50%
Control parallel source filters with morphing
The previous task set up a number of vowel sounds with source filters. Follow these steps to morph between these sounds with your keyboard modulation wheel.
In Logic Pro, click Morph to view morph parameters, then click the Morph Lin button.
Set the X knob to 0%.
In the modulation rack, Morph All X is shown at the top.
Choose Perform > Control7 in the first modulation rack slot. Leave the modulation depth value at 100%.
The modulation wheel is linked by default to performance control 7.
Play your keyboard, and move your modulation wheel to morph between the source filtered sounds.
If the output level seems low, you can boost it by increasing the value of the Vol knob in the Master section or the Volume knob on the Name bar.